Genetic diversity of ruminant Pestivirus strains collected in Northern Ireland between 1999 and 2011 and the role of live ruminant imports
- PMID: 27354911
- PMCID: PMC4924319
- DOI: 10.1186/s13620-016-0066-5
Genetic diversity of ruminant Pestivirus strains collected in Northern Ireland between 1999 and 2011 and the role of live ruminant imports
Abstract
Background: The genus pestivirus within the family Flaviviridae includes bovine viral diarrhoea virus (BVDV) types 1 and 2, border disease virus (BDV) and classical swine fever virus. The two recognised genotypes of BVDV are divided into subtypes based on phylogenetic analysis, namely a-p for BVDV-1 and a-c for BVDV-2.
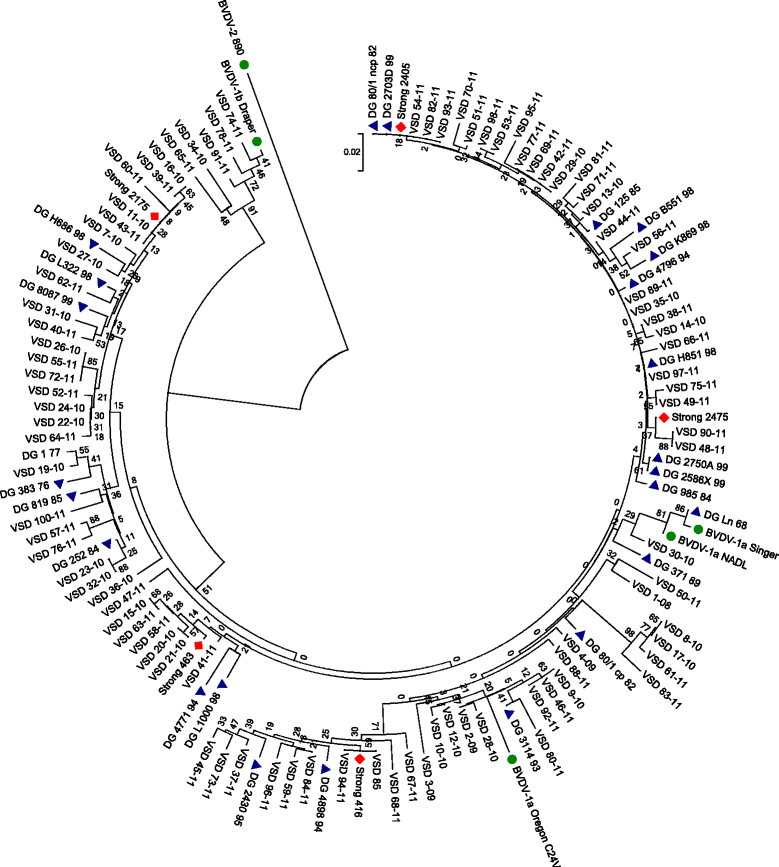
Methods: Three studies were conducted to investigate the phylogenetic diversity of pestiviruses present in Northern Ireland. Firstly, pestiviruses in 152 serum samples that had previously tested positive for BVDV between 1999 and 2008 were genotyped with a RT-PCR assay. Secondly, the genetic heterogeneity of pestiviruses from 91 serum samples collected between 2008 and 2011 was investigated by phylogenetic analysis of a 288 base pair portion of the 5' untranslated region (UTR). Finally, blood samples from 839 bovine and 4,437 ovine animals imported in 2010 and 2011 were tested for pestiviral RNA. Analysis of animal movement data alongside the phylogenetic analysis of the strains was carried out to identify any links between isolates and animal movement.
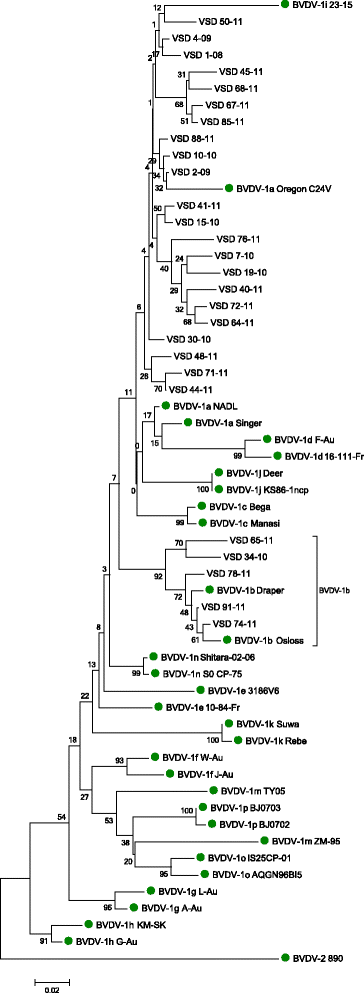
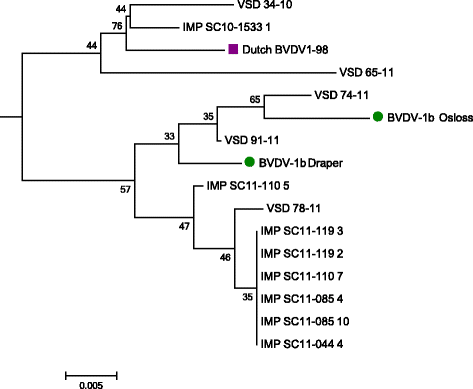
Results: No BVDV-2 strains were detected. All of the 152 samples in the first study were genotyped as BVDV-1. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that the predominant subtype circulating was BVDV-1a (86 samples out of 91). The remaining five samples clustered close to reference strains in subtype BVDV-1b. Out of the imported animals, 18 bovine samples tested positive and 8 inconclusive (Ct ≥36), while all ovine samples were negative. Eight sequences were obtained and were defined as BVDV-1b. Analysis of movement data between herds failed to find links between herds where BVDV-1b was detected.
Conclusion: Given that only BVDV-1a was detected in samples collected between 1968 and 1999, this study suggests that at least one new subtype has been introduced to Northern Ireland between 1999 and 2011 and highlights the potential for importation of cattle to introduce new strains.
Keywords: 5’untranslated region; Bovine viral diarrhoea virus; Importation; Phylogenetic analysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Survey for pestiviruses in backyard pigs in southern Brazil.J Vet Diagn Invest. 2020 Jan;32(1):136-141. doi: 10.1177/1040638719896303. Epub 2020 Jan 10. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2020. PMID: 31924139 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Diversity of Brazilian Bovine Pestiviruses Detected Between 1995 and 2014.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2017 Apr;64(2):613-623. doi: 10.1111/tbed.12427. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2017. PMID: 26415862
-
Nested reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) for typing ruminant pestiviruses: bovine viral diarrhea viruses and border disease virus.Can J Vet Res. 1999 Oct;63(4):276-81. Can J Vet Res. 1999. PMID: 10534007 Free PMC article.
-
Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus in Cattle From Mexico: Current Status.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Aug 13;8:673577. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.673577. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34485426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ruminant pestivirus infection in pigs.Rev Sci Tech. 1990 Mar;9(1):151-61. doi: 10.20506/rst.9.1.484. Rev Sci Tech. 1990. PMID: 1966720 Review.
Cited by
-
Control of Bovine Viral Diarrhea.Pathogens. 2018 Mar 8;7(1):29. doi: 10.3390/pathogens7010029. Pathogens. 2018. PMID: 29518049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Northern Ireland Control Programmes for Infectious Cattle Diseases Not Regulated by the EU.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Aug 26;8:694197. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.694197. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34513968 Free PMC article.
-
Variability and Global Distribution of Subgenotypes of Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus.Viruses. 2017 May 26;9(6):128. doi: 10.3390/v9060128. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 28587150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Seroprevalence of bovine viral diarrhea in Camelus dromedarius from Tunisia.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2025 Apr 14;57(3):172. doi: 10.1007/s11250-025-04414-7. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2025. PMID: 40227478
-
The Irish Programme to Eradicate Bovine Viral Diarrhoea Virus-Organization, Challenges, and Progress.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Jun 1;8:674557. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.674557. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34141734 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Drew TW, Sandvik T, Wakeley P, Jones T, Howard P. BVD virus genotype 2 detected in British cattle. Vet Rec. 2002;151:551. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

