Glucocorticoids Have Opposing Effects on Liver Fibrosis in Hepatic Stellate and Immune Cells
- PMID: 27355192
- PMCID: PMC5414623
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2016-1029
Glucocorticoids Have Opposing Effects on Liver Fibrosis in Hepatic Stellate and Immune Cells
Abstract
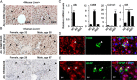
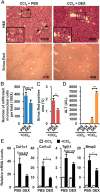
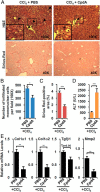
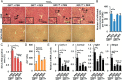
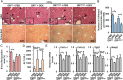
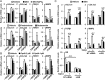
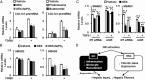
Liver fibrosis is a reversible wound-healing process that is protective in the short term, but prolonged fibrotic responses lead to excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix components that suppresses hepatocyte regeneration, resulting in permanent liver damage. Upon liver damage, nonparenchymal cells including immune cells and hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) have crucial roles in the progression and regression of liver fibrosis. Here, we report differential roles of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), acting in immune cells and HSCs, in liver fibrosis. In the carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxin-induced fibrosis model, both steroidal and nonsteroidal GR ligands suppressed expression of fibrotic genes and decreased extracellular matrix deposition but also inhibited immune cell infiltration and exacerbated liver injury. These counteracting effects of GR ligands were dissociated in mice with conditional GR knockout in immune cells (GR(LysM)) or HSC (GR(hGFAP)): the impacts of dexamethasone on immune cell infiltration and liver injury were totally blunted in GR(LysM) mice, whereas the suppression of fibrotic gene expression was diminished in GR(hGFAP) mice. The effect of GR activation in HSC was further confirmed in the LX-2 HSC cell line, in which antifibrotic effects were mediated by GR ligand inhibition of Sma and mad-related protein 3 (SMAD3) expression. We conclude that GR has differential roles in immune cells and HSCs to modulate liver injury and liver fibrosis. Specific activation of HSC-GR without alteration of GR activity in immune cells provides a potential therapeutic approach to treatment of hepatic fibrosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metformin attenuates motility, contraction, and fibrogenic response of hepatic stellate cells in vivo and in vitro by activating AMP-activated protein kinase.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Feb 21;24(7):819-832. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i7.819. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29467552 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of DJ-1 Ameliorates Liver Fibrosis through Inhibition of Hepatic ROS Production and Inflammation.Int J Biol Sci. 2016 Sep 15;12(10):1225-1235. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.15154. eCollection 2016. Int J Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27766037 Free PMC article.
-
Hesperetin derivative attenuates CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis and inflammation by Gli-1-dependent mechanisms.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Nov;76:105838. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105838. Epub 2019 Aug 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31473406
-
Hepatic fibrosis: It is time to go with hepatic stellate cell-specific therapeutic targets.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2018 Jun;17(3):192-197. doi: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2018.04.003. Epub 2018 Apr 21. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2018. PMID: 29709350 Review.
-
Hepatic stellate cells role in the course of metabolic disorders development - A molecular overview.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Aug;170:105739. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105739. Epub 2021 Jun 23. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 34171492 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Steroid Hormones in the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Metabolites. 2021 May 17;11(5):320. doi: 10.3390/metabo11050320. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34067649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of novel liver-targeting glucocorticoid prodrugs.Med Drug Discov. 2024 Feb;21:100172. doi: 10.1016/j.medidd.2023.100172. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Med Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 38390434 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoids as Regulators of Macrophage-Mediated Tissue Homeostasis.Front Immunol. 2021 May 17;12:669891. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.669891. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34079551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CCL20 and CD8A as potential diagnostic biomarkers for HBV-induced liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 25;10(7):e28329. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28329. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38596115 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of immunomodulators in the treatment of severe COVID-19.J Int Med Res. 2025 Mar;53(3):3000605251317462. doi: 10.1177/03000605251317462. Epub 2025 Mar 13. J Int Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40079461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trautwein C, Friedman SL, Schuppan D, Pinzani M. Hepatic fibrosis: concept to treatment. J Hepatol. 2015;62:S15–S24. - PubMed
-
- Winau F, Hegasy G, Weiskirchen R, et al. . Ito cells are liver-resident antigen-presenting cells for activating T cell responses. Immunity. 2007;26:117–129. - PubMed
-
- Wallace K, Burt AD, Wright MC. Liver fibrosis. Biochem J. 2008;411:1–18. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

