Mining and Analysis of SNP in Response to Salinity Stress in Upland Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.)
- PMID: 27355327
- PMCID: PMC4927152
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158142
Mining and Analysis of SNP in Response to Salinity Stress in Upland Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.)
Abstract
Salinity stress is a major abiotic factor that affects crop output, and as a pioneer crop in saline and alkaline land, salt tolerance study of cotton is particularly important. In our experiment, four salt-tolerance varieties with different salt tolerance indexes including CRI35 (65.04%), Kanghuanwei164 (56.19%), Zhong9807 (55.20%) and CRI44 (50.50%), as well as four salt-sensitive cotton varieties including Hengmian3 (48.21%), GK50 (40.20%), Xinyan96-48 (34.90%), ZhongS9612 (24.80%) were used as the materials. These materials were divided into salt-tolerant group (ST) and salt-sensitive group (SS). Illumina Cotton SNP 70K Chip was used to detect SNP in different cotton varieties. SNPv (SNP variation of the same seedling pre- and after- salt stress) in different varieties were screened; polymorphic SNP and SNPr (SNP related to salt tolerance) were obtained. Annotation and analysis of these SNPs showed that (1) the induction efficiency of salinity stress on SNPv of cotton materials with different salt tolerance index was different, in which the induction efficiency on salt-sensitive materials was significantly higher than that on salt-tolerant materials. The induction of salt stress on SNPv was obviously biased. (2) SNPv induced by salt stress may be related to the methylation changes under salt stress. (3) SNPr may influence salt tolerance of plants by affecting the expression of salt-tolerance related genes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

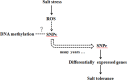
Similar articles
-
Transcriptome analysis reveals that distinct metabolic pathways operate in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive upland cotton varieties subjected to salinity stress.Plant Sci. 2015 Sep;238:33-45. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.05.013. Epub 2015 May 22. Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26259172
-
The cotton WRKY transcription factor GhWRKY17 functions in drought and salt stress in transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana through ABA signaling and the modulation of reactive oxygen species production.Plant Cell Physiol. 2014 Dec;55(12):2060-76. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcu133. Epub 2014 Sep 26. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25261532
-
Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed genes and transcriptional regulation induced by salt stress in two contrasting cotton genotypes.BMC Genomics. 2014 Sep 5;15(1):760. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-760. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25189468 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of salinity stress, mechanism of salinity tolerance and strategies for its management in cotton.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 7;13:907937. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.907937. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36275563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The response of transgenic Brassica species to salt stress: a review.Biotechnol Lett. 2018 Aug;40(8):1159-1165. doi: 10.1007/s10529-018-2570-z. Epub 2018 Jun 1. Biotechnol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29858710 Review.
Cited by
-
Melatonin Improves Cotton Salt Tolerance by Regulating ROS Scavenging System and Ca2 + Signal Transduction.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Jun 28;12:693690. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.693690. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34262587 Free PMC article.
-
GhiPLATZ17 and GhiPLATZ22, zinc-dependent DNA-binding transcription factors, promote salt tolerance in upland cotton.Plant Cell Rep. 2024 May 13;43(6):140. doi: 10.1007/s00299-024-03178-y. Plant Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38740586
-
Genetic dissection of the fuzzless seed trait in Gossypium barbadense.J Exp Bot. 2018 Feb 23;69(5):997-1009. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx459. J Exp Bot. 2018. PMID: 29351643 Free PMC article.
-
GhCLCg-1, a Vacuolar Chloride Channel, Contributes to Salt Tolerance by Regulating Ion Accumulation in Upland Cotton.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Oct 15;12:765173. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.765173. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34721491 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Diversity, QTL Mapping, and Marker-Assisted Selection Technology in Cotton (Gossypium spp.).Front Plant Sci. 2021 Dec 16;12:779386. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.779386. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34975965 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li F, Fan G, Lu C, Xiao G, Zou C, Kohel RJ, et al. Genome sequence of cultivated Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum TM-1) provides insights into genome evolution. Nature Biotechnology. 2015;33(5). - PubMed
-
- Ganal MW, Polley A, Graner EM, Plieske J, Wieseke R, Luerssen H, et al. Large SNP arrays for genotyping in crop plants. Journal of Biosciences. 2012;37(5):821–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

