Testosterone Treatment and Sexual Function in Older Men With Low Testosterone Levels
- PMID: 27355400
- PMCID: PMC4971331
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2016-1645
Testosterone Treatment and Sexual Function in Older Men With Low Testosterone Levels
Abstract
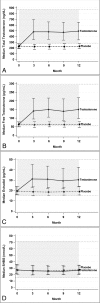
Context: The Testosterone Trials are a coordinated set of seven trials to determine the efficacy of T in symptomatic men ≥65 years old with unequivocally low T levels. Initial results of the Sexual Function Trial showed that T improved sexual activity, sexual desire, and erectile function.
Objective: To assess the responsiveness of specific sexual activities to T treatment; to relate hormone changes to changes in sexual function; and to determine predictive baseline characteristics and T threshold for sexual outcomes.
Design: A placebo-controlled trial.
Setting: Twelve academic medical centers in the United States.
Participants: A total of 470 men ≥65 years of age with low libido, average T <275 ng/dL, and a partner willing to have sexual intercourse at least twice a month.
Methods: Men were assigned to take T gel or placebo for 1 year. Sexual function was assessed by three questionnaires every 3 months: the Psychosexual Daily Questionnaire, the Derogatis Interview for Sexual Function, and the International Index of Erectile Function.
Results: Compared with placebo, T administration significantly improved 10 of 12 measures of sexual activity. Incremental increases in total and free T and estradiol levels were associated with improvements in sexual activity and desire, but not erectile function. No threshold T level was observed for any outcome, and none of the 27 baseline characteristics predicted responsiveness to T.
Conclusions: In older men with low libido and low T levels, improvements in sexual desire and activity in response to T treatment were related to the magnitude of increases in T and estradiol levels, but there was no clear evidence of a threshold effect.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00799617.
Figures
Comment in
-
Re: Testosterone Treatment and Sexual Function in Older Men with Low Testosterone Levels.J Urol. 2016 Dec;196(6):1721-1724. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2016.09.058. Epub 2016 Oct 21. J Urol. 2016. PMID: 27845126 No abstract available.
-
Re: Testosterone Treatment and Sexual Function in Older Men with Low Testosterone Levels.J Urol. 2017 Feb;197(2):495. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2016.11.050. Epub 2016 Nov 15. J Urol. 2017. PMID: 28093177 No abstract available.
References
-
- Burris AS, Banks SM, Carter CS, Davidson JM, Sherins RJ. A long-term, prospective study of the physiologic and behavioral effects of hormone replacement in untreated hypogonadal men. J Androl. 1992;13(4):297–304. - PubMed
-
- Snyder PJ, Peachey H, Berlin JA, et al. Effects of testosterone replacement in hypogonadal men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85(8):2670–2677. - PubMed
-
- Bhasin S, Woodhouse L, Casaburi R, et al. Testosterone dose-response relationships in healthy young men. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2001;281(6):E1172–E1181. - PubMed
-
- Finkelstein JS, Yu EW, Burnett-Bowie SA. Gonadal steroids and body composition, strength, and sexual function in men. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(25):2457. - PubMed
-
- Bagatell CJ, Heiman JR, Rivier JE, Bremner WJ. Effects of endogenous testosterone and estradiol on sexual behavior in normal young men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994;78(3):711–716. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical