Option B+ in Mozambique: Formative Research Findings for the Design of a Facility-Level Clustered Randomized Controlled Trial to Improve ART Retention in Antenatal Care
- PMID: 27355507
- PMCID: PMC5113244
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000001061
Option B+ in Mozambique: Formative Research Findings for the Design of a Facility-Level Clustered Randomized Controlled Trial to Improve ART Retention in Antenatal Care
Abstract
Introduction: With the rollout of "Option B+" in Mozambique in 2013, initial data indicated major challenges to early retention in antiretroviral therapy (ART) among HIV-positive pregnant women. We sought to develop and test a pilot intervention in 6 large public clinics in central Mozambique to improve retention of mothers starting ART in antenatal care. The results from the formative research from this study described here were used to design the intervention.
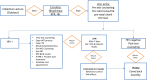
Methods: The research was initiated in early 2013 and completed in early 2014 in each of the 6 study clinics and consisted of (1) patient flow mapping and measurement of retention through collection of health systems data from antenatal care registries, pharmacy registries, ART clinic databases, (2) workforce assessment and measurement of patient waiting times, and (3) patient and worker individual interviews and focus groups.
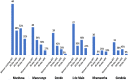
Results: Coverage of HIV testing and ART initiation were over 90% at all sites, but retention at 30-, 60-, and 90-day pharmacy refill visits was very low ranging from only 5% at 1 site to 30% returning at 90 days. These data revealed major systemic bottlenecks that contributed to poor adherence and retention in the first month after ART initiation. Long wait times, short consultations, and poor counseling were identified as barriers.
Conclusions: Based on these findings, we designed an intervention with these components: (1) workflow modification to redefine nurse tasks, shift tasks to community health workers, and enhance patient tracking and (2) an adherence and retention package to systematize active patient follow-up, ensure home visits by community health workers, use text messaging, and intensify counseling by health staff. This intervention is currently under evaluation using a stepped wedge design.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Barker PM, Mphatswe W, Rollins N. Antiretroviral drugs in the cupboard are not enough: the impact of health systems' performance on mother-to-child transmission of HIV. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2011;56:e45–e48. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson L, Lewis J, Grant AD, et al. Patient attrition between diagnosis with HIV in pregnancy-related services and long-term HIV care and treatment services in Kenya: a retrospective study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2012;60:e90–e97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical