Metabolism of 4-Hydroxy-7-oxo-5-heptenoic Acid (HOHA) Lactone by Retinal Pigmented Epithelial Cells
- PMID: 27355557
- PMCID: PMC5008261
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.6b00153
Metabolism of 4-Hydroxy-7-oxo-5-heptenoic Acid (HOHA) Lactone by Retinal Pigmented Epithelial Cells
Abstract
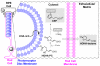
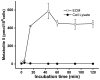
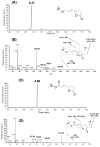
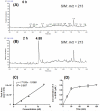
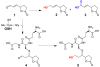
4-Hydroxy-7-oxo-5-heptenic acid (HOHA)-lactone is a biologically active oxidative truncation product released (t1/2 = 30 min at 37 °C) by nonenzymatic transesterification/deacylation from docosahexaenoate lipids. We now report that HOHA-lactone readily diffuses into retinal pigmented epithelial (RPE) cells where it is metabolized. A reduced glutathione (GSH) Michael adduct of HOHA-lactone is the most prominent metabolite detected by LC-MS in both the extracellular medium and cell lysates. This molecule appeared inside of ARPE-19 cells within seconds after exposure to HOHA-lactone. The intracellular level reached a maximum concentration at 30 min and then decreased with concomitant increases in its level in the extracellular medium, thus revealing a unidirectional export of the reduced GSH-HOHA-lactone adduct from the cytosol to extracellular medium. This metabolism is likely to modulate the involvement of HOHA-lactone in the pathogenesis of human diseases. HOHA-lactone is biologically active, e.g., low concentrations (0.1-1 μM) induce secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) from ARPE-19 cells. HOHA-lactone is also a precursor of 2-(ω-carboxyethyl)pyrrole (CEP) derivatives of primary amino groups in proteins and ethanolamine phospholipids that have significant pathological and physiological relevance to age-related macular degeneration (AMD), cancer, and wound healing. Both HOHA-lactone and the derived CEP can contribute to the angiogenesis that defines the neovascular "wet" form of AMD and that promotes the growth of tumors. While GSH depletion can increase the lethality of radiotherapy, because it will impair the metabolism of HOHA-lactone, the present study suggests that GSH depletion will also increase levels of HOHA-lactone and CEP that may promote recurrence of tumor growth.
Figures





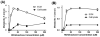
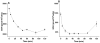



Similar articles
-
4-Hydroxy-7-oxo-5-heptenoic Acid Lactone Induces Angiogenesis through Several Different Molecular Pathways.Chem Res Toxicol. 2016 Dec 19;29(12):2125-2135. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.6b00233. Epub 2016 Nov 11. Chem Res Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27806561 Free PMC article.
-
4-Hydroxy-7-oxo-5-heptenoic Acid (HOHA) Lactone is a Biologically Active Precursor for the Generation of 2-(ω-Carboxyethyl)pyrrole (CEP) Derivatives of Proteins and Ethanolamine Phospholipids.Chem Res Toxicol. 2015 May 18;28(5):967-77. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.5b00001. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Chem Res Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25793308 Free PMC article.
-
4-Hydroxy-7-oxo-5-heptenoic acid lactone can induce mitochondrial dysfunction in retinal pigmented epithelial cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2020 Nov 20;160:719-733. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.09.009. Epub 2020 Sep 10. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32920040 Free PMC article.
-
4-Hydroxy-7-oxo-5-heptenoic acid (HOHA) lactone induces apoptosis in retinal pigment epithelial cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2020 May 20;152:280-294. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.03.017. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32222470 Free PMC article.
-
Stem cell based therapies for age-related macular degeneration: The promises and the challenges.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2015 Sep;48:1-39. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2015.06.004. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2015. PMID: 26113213 Review.
Cited by
-
4-Hydroxy-7-oxo-5-heptenoic Acid Lactone Is a Potent Inducer of the Complement Pathway in Human Retinal Pigmented Epithelial Cells.Chem Res Toxicol. 2018 Aug 20;31(8):666-679. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.8b00028. Epub 2018 Jul 9. Chem Res Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29883119 Free PMC article.
-
Carboxyethylpyrroles: From Hypothesis to the Discovery of Biologically Active Natural Products.Chem Res Toxicol. 2017 Jan 17;30(1):105-113. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.6b00304. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Chem Res Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27750413 Free PMC article.
-
Light-induced generation and toxicity of docosahexaenoate-derived oxidation products in retinal pigmented epithelial cells.Exp Eye Res. 2019 Apr;181:325-345. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2018.09.012. Epub 2018 Oct 5. Exp Eye Res. 2019. PMID: 30296412 Free PMC article.
-
Cysteinyl leukotriene-like metabolites are generated in retinal pigment epithelial cells through glutathionylation/reduction of an oxidatively truncated fragment of arachidonate.Results Chem. 2023 Dec;6:100995. doi: 10.1016/j.rechem.2023.100995. Epub 2023 Jun 11. Results Chem. 2023. PMID: 38855016 Free PMC article.
-
4-Hydroxy-7-oxo-5-heptenoic Acid Lactone Induces Angiogenesis through Several Different Molecular Pathways.Chem Res Toxicol. 2016 Dec 19;29(12):2125-2135. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.6b00233. Epub 2016 Nov 11. Chem Res Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27806561 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang H, Linetsky M, Guo J, Choi J, Hong L, Chamberlain AS, Howell SJ, Howes AM, Salomon RG. 4-Hydroxy-7-oxo-5-heptenoic Acid (HOHA) Lactone is a Biologically Active Precursor for the Generation of 2-(omega-Carboxyethyl)pyrrole (CEP) Derivatives of Proteins and Ethanolamine Phospholipids. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015;28:967–977. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gu X, Meer SG, Miyagi M, Rayborn ME, Hollyfield JG, Crabb JW, Salomon RG. Carboxyethylpyrrole protein adducts and autoantibodies, biomarkers for age-related macular degeneration. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:42027–42035. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

