Site-Specific Labeling of Protein Kinase CK2: Combining Surface Display and Click Chemistry for Drug Discovery Applications
- PMID: 27355959
- PMCID: PMC5039489
- DOI: 10.3390/ph9030036
Site-Specific Labeling of Protein Kinase CK2: Combining Surface Display and Click Chemistry for Drug Discovery Applications
Abstract
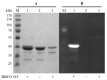
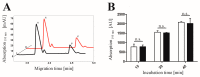
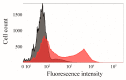
Human CK2 is a heterotetrameric constitutively active serine/threonine protein kinase and is an emerging target in current anti-cancer drug discovery. The kinase is composed of two catalytic CK2α subunits and two regulatory CK2β subunits. In order to establish an assay to identify protein-protein-interaction inhibitors (PPI) of the CK2α/CK2β interface, a bioorthogonal click reaction was used to modify the protein kinase α-subunit with a fluorophore. By expanding the genetic code, the unnatural amino acid para azidophenylalanine (pAzF) could be incorporated into CK2α. Performing the SPAAC click reaction (Strain-Promoted Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition) by the use of a dibenzylcyclooctyne-fluorophore (DBCO-fluorophore) led to a specifically labeled human protein kinase CK2α. This site-specific labeling does not impair the phosphorylation activity of CK2, which was evaluated by capillary electrophoresis. Furthermore a dissociation constant (KD) of 631 ± 86.2 nM was determined for the substrate αS1-casein towards CK2α. This labeling strategy was also applied to CK2β subunit on Escherichia coli, indicating the site-specific modifications of proteins on the bacterial cell surface when displayed by Autodisplay.
Keywords: Autodisplay; CK2; bioorthogonal; click chemistry; drug discovery; kinase; labeling; protein-protein interaction; unnatural amino acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Toward selective CK2alpha and CK2alpha' inhibitors: Development of a novel whole-cell kinase assay by Autodisplay of catalytic CK2alpha'.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016 Mar 20;121:253-260. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2016.01.011. Epub 2016 Jan 8. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016. PMID: 26786382
-
Functional display of heterotetrameric human protein kinase CK2 on Escherichia coli: a novel tool for drug discovery.Microb Cell Fact. 2015 Jun 3;14:74. doi: 10.1186/s12934-015-0263-z. Microb Cell Fact. 2015. PMID: 26036951 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Activity Relationship Studies of Tetracyclic Pyrrolocarbazoles Inhibiting Heterotetrameric Protein Kinase CK2.Molecules. 2024 Dec 27;30(1):63. doi: 10.3390/molecules30010063. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39795120 Free PMC article.
-
Ecto-protein kinase CK2, the neglected form of CK2.Biomed Rep. 2018 Apr;8(4):307-313. doi: 10.3892/br.2018.1069. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Biomed Rep. 2018. PMID: 29556379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein kinase CK2 and ion channels (Review).Biomed Rep. 2020 Dec;13(6):55. doi: 10.3892/br.2020.1362. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Biomed Rep. 2020. PMID: 33082952 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of a Potent Allosteric Inhibitor of Human Protein Kinase CK2 by Bacterial Surface Display Library Screening.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2017 Jan 5;10(1):6. doi: 10.3390/ph10010006. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28067769 Free PMC article.
-
Photobodies: Light-Activatable Single-Domain Antibody Fragments.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020 Jan 20;59(4):1506-1510. doi: 10.1002/anie.201912286. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020. PMID: 31755215 Free PMC article.
-
De novo variants of CSNK2B cause a new intellectual disability-craniodigital syndrome by disrupting the canonical Wnt signaling pathway.HGG Adv. 2022 Apr 18;3(3):100111. doi: 10.1016/j.xhgg.2022.100111. eCollection 2022 Jul 14. HGG Adv. 2022. PMID: 35571680 Free PMC article.
-
Binding Affinity Quantifications of the Bacteriophage Mu DNA Modification Protein Mom Using Microscale Thermophoresis (MST).Bio Protoc. 2022 Jul 20;12(14):e4472. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4472. eCollection 2022 Jul 20. Bio Protoc. 2022. PMID: 35978573 Free PMC article.
-
ITC-derived binding affinity may be biased due to titrant (nano)-aggregation. Binding of halogenated benzotriazoles to the catalytic domain of human protein kinase CK2.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 8;12(3):e0173260. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173260. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28273138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burnett G., Kennedy E.P. The enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1954;211:969–980. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

