Acetylated tau destabilizes the cytoskeleton in the axon initial segment and is mislocalized to the somatodendritic compartment
- PMID: 27356871
- PMCID: PMC4928318
- DOI: 10.1186/s13024-016-0109-0
Acetylated tau destabilizes the cytoskeleton in the axon initial segment and is mislocalized to the somatodendritic compartment
Abstract
Background: Neurons are highly polarized cells in which asymmetric axonal-dendritic distribution of proteins is crucial for neuronal function. Loss of polarized distribution of the axonal protein tau is an early sign of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and other neurodegenerative disorders. The cytoskeletal network in the axon initial segment (AIS) forms a barrier between the axon and the somatodentritic compartment, contributing to axonal retention of tau. Although perturbation of the AIS cytoskeleton has been implicated in neurological disorders, the molecular triggers and functional consequence of AIS perturbation are incompletely understood.
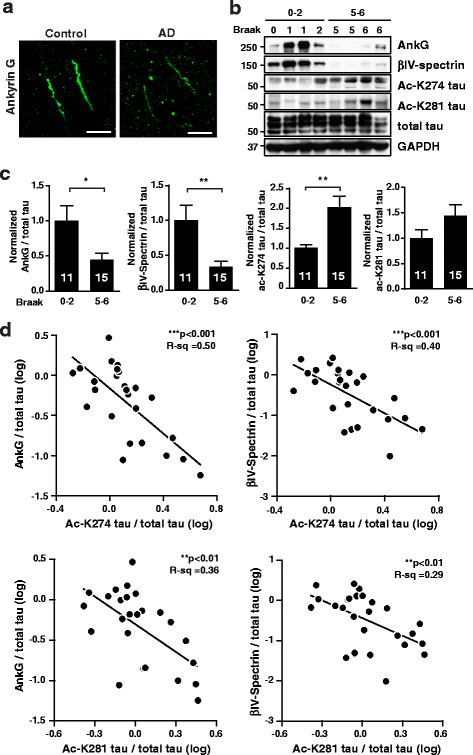
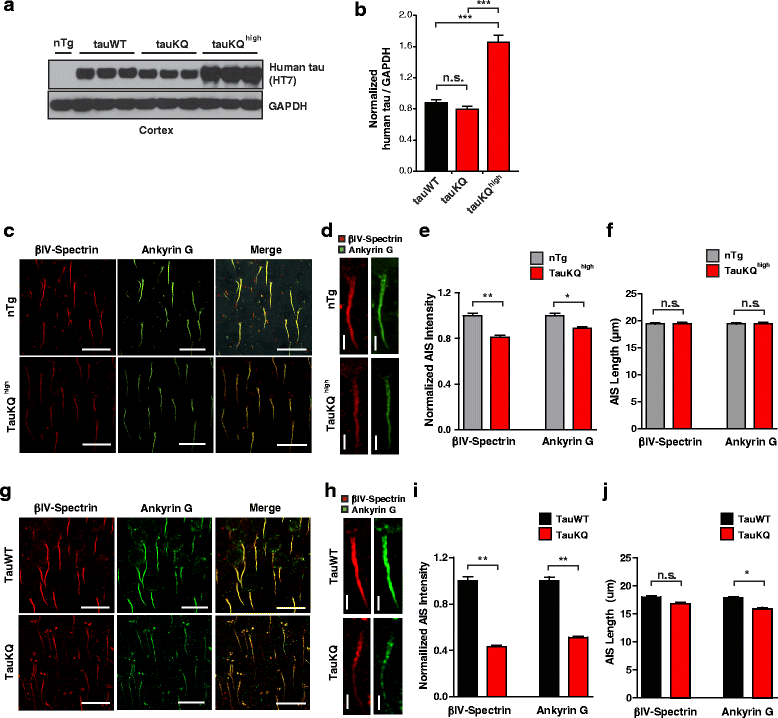
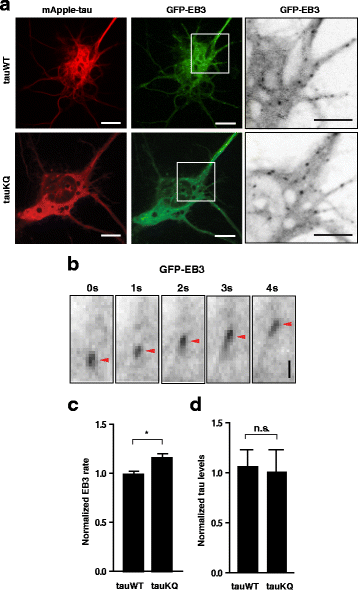
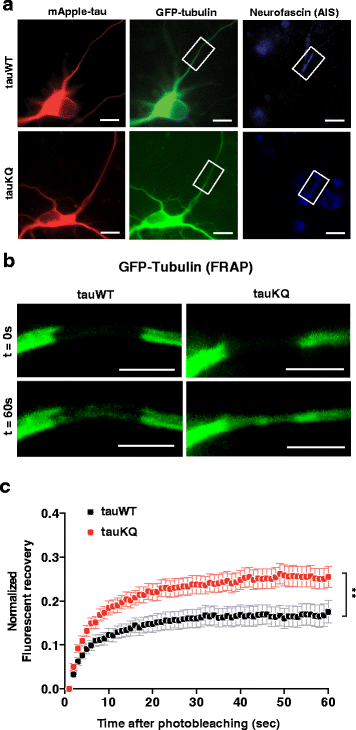
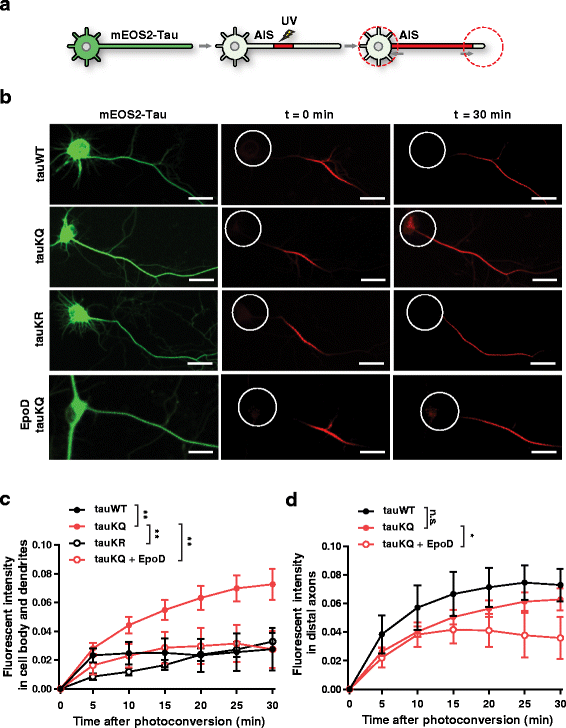
Results: Here we report that tau acetylation and consequent destabilization of the AIS cytoskeleton promote the somatodendritic mislocalization of tau. AIS cytoskeletal proteins, including ankyrin G and βIV-spectrin, were downregulated in AD brains and negatively correlated with an increase in tau acetylated at K274 and K281. AIS proteins were also diminished in transgenic mice expressing tauK274/281Q, a tau mutant that mimics K274 and K281 acetylation. In primary neuronal cultures, the tauK274/281Q mutant caused hyperdynamic microtubules (MTs) in the AIS, shown by live-imaging of MT mobility and fluorescence recovery after photobleaching. Using photoconvertible tau constructs, we found that axonal tauK274/281Q was missorted into the somatodendritic compartment. Stabilizing MTs with epothilone D to restore the cytoskeletal barrier in the AIS prevented tau mislocalization in primary neuronal cultures.
Conclusions: Together, these findings demonstrate that tau acetylation contributes to the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disease by compromising the cytoskeletal sorting machinery in the AIS.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Axon initial segment; Neuronal cytoskeleton; Neuronal polarity; Tau acetylation.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

