Multiple cone pathways are involved in photic regulation of retinal dopamine
- PMID: 27356880
- PMCID: PMC4928117
- DOI: 10.1038/srep28916
Multiple cone pathways are involved in photic regulation of retinal dopamine
Abstract
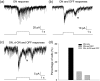
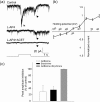
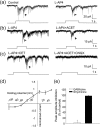
Dopamine is a key neurotransmitter in the retina and plays a central role in the light adaptive processes of the visual system. The sole source of retinal dopamine is dopaminergic amacrine cells (DACs). We and others have previously demonstrated that DACs are activated by rods, cones, and intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs) upon illumination. However, it is still not clear how each class of photosensitive cells generates light responses in DACs. We genetically isolated cone function in mice to specifically examine the cone-mediated responses of DACs and their neural pathways. In addition to the reported excitatory input to DACs from light-increment (ON) bipolar cells, we found that cones alternatively signal to DACs via a retrograde signalling pathway from ipRGCs. Cones also produce ON and light-decrement (OFF) inhibitory responses in DACs, which are mediated by other amacrine cells, likely driven by type 1 and type 2/3a OFF bipolar cells, respectively. Dye injections indicated that DACs had similar morphological profiles with or without ON/OFF inhibition. Our data demonstrate that cones utilize specific parallel excitatory and inhibitory circuits to modulate DAC activity and efficiently regulate dopamine release and the light-adaptive state of the retina.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Mapping physiological inputs from multiple photoreceptor systems to dopaminergic amacrine cells in the mouse retina.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 11;7(1):7920. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08172-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28801634 Free PMC article.
-
Orexin-A Suppresses Signal Transmission to Dopaminergic Amacrine Cells From Outer and Inner Retinal Photoreceptors.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017 Sep 1;58(11):4712-4721. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-21835. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28910447 Free PMC article.
-
M1 ipRGCs Influence Visual Function through Retrograde Signaling in the Retina.J Neurosci. 2016 Jul 6;36(27):7184-97. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3500-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27383593 Free PMC article.
-
Light-dependent pathways for dopaminergic amacrine cell development and function.Elife. 2018 Nov 7;7:e39866. doi: 10.7554/eLife.39866. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30403373 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells.Sci China Life Sci. 2010 Jan;53(1):58-67. doi: 10.1007/s11427-010-0024-5. Epub 2010 Feb 12. Sci China Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20596956 Review.
Cited by
-
Dim Light Exposure and Myopia in Children.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Oct 1;59(12):4804-4811. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-24415. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 30347074 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of GluA2-containing calcium-impermeable AMPA receptors on dopaminergic amacrine cells in the mouse retina.Mol Vis. 2019 Nov 19;25:780-790. eCollection 2019. Mol Vis. 2019. PMID: 31819340 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Applications of the Cone Contrast Test in Ophthalmology and Neurology.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 29;14(9):3079. doi: 10.3390/jcm14093079. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40364109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of GJD2(Cx36) in Refractive Error Development.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022 Mar 2;63(3):5. doi: 10.1167/iovs.63.3.5. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022. PMID: 35262731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping physiological inputs from multiple photoreceptor systems to dopaminergic amacrine cells in the mouse retina.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 11;7(1):7920. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08172-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28801634 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weiler R., Kohler K., Kirsch M. & Wagner H. J. Glutamate and dopamine modulate synaptic plasticity in horizontal cell dendrites of fish retina. Neuroscience letters 87, 205–209 (1988). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

