MCOLN1 is a ROS sensor in lysosomes that regulates autophagy
- PMID: 27357649
- PMCID: PMC4931332
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms12109
MCOLN1 is a ROS sensor in lysosomes that regulates autophagy
Abstract
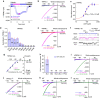
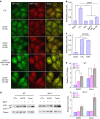
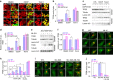
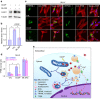
Cellular stresses trigger autophagy to remove damaged macromolecules and organelles. Lysosomes 'host' multiple stress-sensing mechanisms that trigger the coordinated biogenesis of autophagosomes and lysosomes. For example, transcription factor (TF)EB, which regulates autophagy and lysosome biogenesis, is activated following the inhibition of mTOR, a lysosome-localized nutrient sensor. Here we show that reactive oxygen species (ROS) activate TFEB via a lysosomal Ca(2+)-dependent mechanism independent of mTOR. Exogenous oxidants or increasing mitochondrial ROS levels directly and specifically activate lysosomal TRPML1 channels, inducing lysosomal Ca(2+) release. This activation triggers calcineurin-dependent TFEB-nuclear translocation, autophagy induction and lysosome biogenesis. When TRPML1 is genetically inactivated or pharmacologically inhibited, clearance of damaged mitochondria and removal of excess ROS are blocked. Furthermore, TRPML1's ROS sensitivity is specifically required for lysosome adaptation to mitochondrial damage. Hence, TRPML1 is a ROS sensor localized on the lysosomal membrane that orchestrates an autophagy-dependent negative-feedback programme to mitigate oxidative stress in the cell.
Figures


References
-
- Scherz-Shouval R. & Elazar Z. Regulation of autophagy by ROS: physiology and pathology. Trends Biochem. Sci. 36, 30–38 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Barnham K. J., Masters C. L. & Bush A. I. Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative stress. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 3, 205–214 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Wang Y., Nartiss Y., Steipe B., McQuibban G. A. & Kim P. K. ROS-induced mitochondrial depolarization initiates PARK2/PARKIN-dependent mitochondrial degradation by autophagy. Autophagy 8, 1462–1476 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

