High-mobility group box 1 inhibits HCO3- absorption in the medullary thick ascending limb through RAGE-Rho-ROCK-mediated inhibition of basolateral Na+/H+ exchange
- PMID: 27358052
- PMCID: PMC5142168
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00185.2016
High-mobility group box 1 inhibits HCO3- absorption in the medullary thick ascending limb through RAGE-Rho-ROCK-mediated inhibition of basolateral Na+/H+ exchange
Abstract
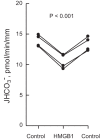
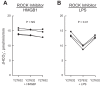
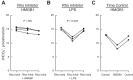
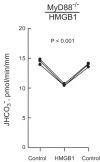
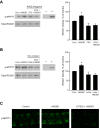
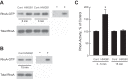
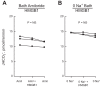
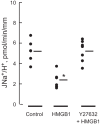
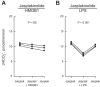
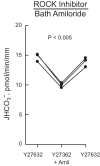
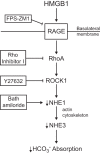
High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) is a nuclear protein released extracellularly in response to infection or injury, where it activates immune responses and contributes to the pathogenesis of kidney dysfunction in sepsis and sterile inflammatory disorders. Recently, we demonstrated that HMGB1 inhibits HCO3 (-) absorption in perfused rat medullary thick ascending limbs (MTAL) through a basolateral receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE)-dependent pathway that is additive to Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-ERK-mediated inhibition by LPS (Good DW, George T, Watts BA III. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 309: F720-F730, 2015). Here, we examined signaling and transport mechanisms that mediate inhibition by HMGB1. Inhibition of HCO3 (-) absorption by HMGB1 was eliminated by the Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) inhibitor Y27632 and by a specific inhibitor of Rho, the major upstream activator of ROCK. HMGB1 increased RhoA and ROCK1 activity. HMGB1-induced ROCK1 activation was eliminated by the RAGE antagonist FPS-ZM1 and by inhibition of Rho. The Rho and ROCK inhibitors had no effect on inhibition of HCO3 (-) absorption by bath LPS. Inhibition of HCO3 (-) absorption by HMGB1 was eliminated by bath amiloride, 0 Na(+) bath, and the F-actin stabilizer jasplakinolide, three conditions that selectively prevent inhibition of MTAL HCO3 (-) absorption mediated through NHE1. HMGB1 decreased basolateral Na(+)/H(+) exchange activity through activation of ROCK. We conclude that HMGB1 inhibits HCO3 (-) absorption in the MTAL through a RAGE-RhoA-ROCK1 signaling pathway coupled to inhibition of NHE1. The HMGB1-RAGE-RhoA-ROCK1 pathway thus represents a potential target to attenuate MTAL dysfunction during sepsis and other inflammatory disorders. HMGB1 and LPS inhibit HCO3 (-) absorption through different receptor signaling and transport mechanisms, which enables these pathogenic mediators to act directly and independently to impair MTAL function.
Keywords: HMGB1; NHE1; ROCK; kidney; sepsis.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

