Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-sialylated mucin core polypeptide 1 is a sensitive biomarker for biliary tract carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a multicenter study
- PMID: 27358229
- PMCID: PMC5281651
- DOI: 10.1007/s00535-016-1230-0
Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-sialylated mucin core polypeptide 1 is a sensitive biomarker for biliary tract carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a multicenter study
Abstract
Background: Wisteria floribunda agglutinin (WFA)-sialylated mucin core polypeptide 1 (MUC1) was investigated as a new glycoprotein marker for cholangiocarcinoma (CC) using glycoproteomics technologies. In this multicenter study, WFA-sialylated MUC1 levels in serum and bile samples were measured to determine their diagnostic capability in biliary tract carcinoma (BTC) and intrahepatic (Ih) CC.
Methods: The study included 244 patients with BTC, 59 patients with IhCC, 287 patients with benign biliary tract diseases, and 44 control subjects.
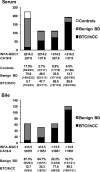
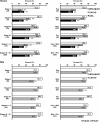
Results: Serum WFA-sialylated MUC1 levels were significantly higher in patients with either BTC or IhCC than in control subjects and those with benign biliary tract diseases. Patients with IhCC showed higher WFA-sialylated MUC1 levels than patients with tumors at other sites. No significant differences in WFA-sialylated MUC1 levels were found with regard to cancer stage or tissue type. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed that WFA-sialylated MUC1 was superior to carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) for the diagnosis of benign biliary tract diseases, BTC, and IhCC, as well as for stage I and II carcinomas. Significantly higher levels of biliary WFA-sialylated MUC1 were observed in BTC/IhCC than in benign biliary tract diseases. The diagnostic capability of biliary WFA-sialylated MUC1 was also superior to that of CA19-9, and diagnostic sensitivity was higher than that of biliary cytology for BTC/IhCC.
Conclusions: WFA-sialylated MUC1 is a useful novel biomarker for BTC/IhCC. In the future, this measurement should be applied in the clinical setting.
Keywords: Biliary tract carcinoma; Biomarker; Glycoproteomics; Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; Multicenter study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. Financial support This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-aid from the National Survey for Intractable Hepatobiliary Diseases from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan, and a Grant-in-aid for scientific research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan (Nos. 24390323 and 15K10197).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Meta-analysis of the diagnostic value of Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-sialylated mucin1 and the prognostic role of mucin1 in human cholangiocarcinoma.BMJ Open. 2019 Jan 29;9(1):e021693. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-021693. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 30700476 Free PMC article.
-
Verification of WFA-Sialylated MUC1 as a Sensitive Biliary Biomarker for Human Biliary Tract Cancer.Ann Surg Oncol. 2016 Feb;23(2):671-7. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4878-4. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26416714
-
Glycoproteomics-based cancer marker discovery adopting dual enrichment with Wisteria floribunda agglutinin for high specific glyco-diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma.J Proteomics. 2013 Jun 24;85:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.04.017. Epub 2013 Apr 21. J Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23612463 Clinical Trial.
-
Wisteria floribunda agglutinin positive glycobiomarkers: a unique lectin as a serum biomarker probe in various diseases.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2018 Feb;15(2):183-190. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2018.1419066. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 29265940 Review.
-
Biliary brushing cytology.Cytopathology. 2004 Apr;15(2):74-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2303.2004.00133.x. Cytopathology. 2004. PMID: 15056166 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of tumor characteristics based on glycoform analysis of membrane-tethered MUC1.Lab Invest. 2017 Sep;97(9):1103-1113. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2017.53. Epub 2017 Jun 5. Lab Invest. 2017. PMID: 28581490
-
Serum Wisteria Floribunda Agglutinin-Positive Sialylated Mucin 1 as a Marker of Progenitor/Biliary Features in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 21;7(1):244. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00357-8. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28325920 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of the diagnostic value of Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-sialylated mucin1 and the prognostic role of mucin1 in human cholangiocarcinoma.BMJ Open. 2019 Jan 29;9(1):e021693. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-021693. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 30700476 Free PMC article.
-
Mucins: the Old, the New and the Promising Factors in Hepatobiliary Carcinogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 14;20(6):1288. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061288. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30875782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The diagnostic and prognostic value of UBE2T in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.PeerJ. 2020 Jan 27;8:e8454. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8454. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32025379 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Bray F, Pisani P, et al. GLOBOCAN 2002. Cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence worldwide. IARC CancerBase No. 5, version 2.0. Lyon: IARC Press; 2004.
-
- Division of Vital Statistics, Statistics and Information Department, Minister’s Secretariat, Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW): http://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/saikin/index.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

