HER3 Targeting Sensitizes HNSCC to Cetuximab by Reducing HER3 Activity and HER2/HER3 Dimerization: Evidence from Cell Line and Patient-Derived Xenograft Models
- PMID: 27358485
- PMCID: PMC5199640
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0558
HER3 Targeting Sensitizes HNSCC to Cetuximab by Reducing HER3 Activity and HER2/HER3 Dimerization: Evidence from Cell Line and Patient-Derived Xenograft Models
Abstract
Purpose: Our previous work suggested that HER3 inhibition sensitizes head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) to EGFR inhibition with cetuximab. This study aimed to define the role of HER3 in cetuximab resistance and the antitumor mechanisms of EGFR/HER3 dual targeting in HNSCC.
Experimental design: We treated cetuximab-resistant HNSCC UMSCC1-C and parental UMSCC1-P cell lines with anti-EGFR antibody cetuximab, anti-HER3 antibody MM-121, and their combination. We assessed activities of HER2, HER3, and downstream signaling pathways by Western blotting and cell growth by sulforhodamine B (SRB) and colony formation assays. HER3-specific shRNA was used to confirm the role of HER3 in cetuximab response. The combined efficacy and alterations in biomarkers were evaluated in UMSCC1-C xenograft and patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models.
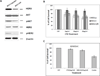
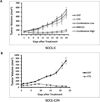
Results: Cetuximab treatment induced HER3 activation and HER2/HER3 dimerization in HNSCC cell lines. Combined treatment with cetuximab and MM-121 blocked EGFR and HER3 activities and inhibited the PI3K/AKT and ERK signaling pathways and HNSCC cell growth more effectively than each antibody alone. HER3 knockdown reduced HER2 activation and resensitized cells to cetuximab. Cetuximab-resistant xenografts and PDX models revealed greater efficacy of dual EGFR and HER3 inhibition compared with single antibodies. In PDX tissue samples, cetuximab induced HER3 expression and MM-121 reduced AKT activity.
Conclusions: Clinically relevant PDX models demonstrate that dual targeting of EGFR and HER3 is superior to EGFR targeting alone in HNSCC. Our study illustrates the upregulation of HER3 by cetuximab as one mechanism underlying resistance to EGFR inhibition in HNSCC, supporting further clinical investigations using multiple targeting strategies in patients who have failed cetuximab-based therapy. Clin Cancer Res; 23(3); 677-86. ©2016 AACR.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
of Potential Conflicts of Interest No potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures






References
-
- Ongkeko WM, Altuna X, Weisman RA, Wang-Rodriguez J. Expression of protein tyrosine kinases in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Am J Clin Pathol. 2005;124:71–76. - PubMed
-
- Bei R, Budillon A, Masuelli L, Cereda V, Vitolo D, et al. Frequent overexpression of multiple ErbB receptors by head and neck squamous cell carcinoma contrasts with rare antibody immunity in patients. J Pathol. 2004;204:317–325. - PubMed
-
- Vermorken JB, Mesia R, Rivera F, Remenar E, Kawecki A, et al. Platinum-based chemotherapy plus cetuximab in head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1116–1127. - PubMed
-
- Vermorken JB, Trigo J, Hitt R, Koralewski P, Diaz-Rubio E, et al. Open-label, uncontrolled, multicenter phase II study to evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of cetuximab as a single agent in patients with recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck who failed to respond to platinum-based therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:2171–2177. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

