Effectiveness of a thoracic multidisciplinary clinic in the treatment of stage III non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 27358568
- PMCID: PMC4912343
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S98345
Effectiveness of a thoracic multidisciplinary clinic in the treatment of stage III non-small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
Introduction: The Institute of Medicine, the American Society of Clinical Oncology, and the European Society of Medical Oncology promote a multidisciplinary approach for the treatment of cancer. Stage III non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) represents a heterogeneous group of diseases necessitating coordination of care among medical, radiation, and surgical oncology. The optimal care of stage III NSCLC underscores the need for a multidisciplinary approach.
Methods: From tumor registry data, we identified all cases of stage III NSCLC seen at Lehigh Valley Health Network between March 2010 and March 2013. The care received by patients when seen in the thoracic multidisciplinary clinic (MDC) was compared with the care received when not seen in the thoracic MDC.
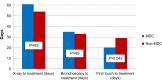
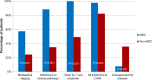
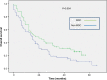
Results: All patients seen in the MDC, compared to <50% of patients seen outside the MDC, were evaluated by more than one physician prior to beginning the treatment. Time to initiate treatment was shorter in MDC patients than in non-MDC patients. Patients seen in the MDC had a greater concordance with clinical pathways. A greater percentage of patients seen in the thoracic MDC had pathologic staging of their mediastinum. Patients seen in the MDC were more likely to receive all of their care at Lehigh Valley Health Network.
Conclusion: Multidisciplinary care is essential in the treatment of patients with stage III NSCLC. Greater utilization of MDCs for this complex group of patients will result in more efficient coordination of care, pretreatment evaluation, and therapy, which in turn should translate to improve patients' outcomes.
Keywords: clinical pathways; lung cancer; multidisciplinary care.
Figures
References
-
- Levit BL, Nass S, Ganz PA, editors. Delivering High-Quality Cancer Care: Charting a New Course for a System in Crisis. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2013. - PubMed
-
- American Society of Clinical Oncology European Society for Medical Oncology. ASCO-ESMO consensus statement on quality cancer care. Ann Oncol. 2006;17(7):1063–1064. - PubMed
-
- Tripathy D. Multidisciplinary care for breast cancer: barriers and solutions. Breast J. 2003;9(1):60–63. - PubMed
-
- Frost MH, Arvizu RD, Jayakumar S, Schoonover A, Novotny P, Zahasky K. A multidisciplinary healthcare delivery model for women with breast cancer: patient satisfaction and physical and psychosocial adjustment. Oncol Nurs Forum. 1999;26(10):1673–1680. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

