Awareness and practices on eye effects among people with diabetes in rural Tamil Nadu, India
- PMID: 27358634
- PMCID: PMC4915436
- DOI: 10.4314/ahs.v16i1.28
Awareness and practices on eye effects among people with diabetes in rural Tamil Nadu, India
Abstract
Background: Recently eye effects of Diabetes Mellitus (DM) are an important concern due to increase in its trend especially in developing countries.
Objectives: To assess the awareness related to eye effects of DM and its prevention practices among people with diabetes.
Methods: This cross sectional study was conducted from January 2013 to April 2013 in Villupuram district of Tamil Nadu, India. All 105 people with diabetes from the service area of two sub-centres were included. Data on socio demographic details, history of DM, awareness on systemic complications of DM, effects of DM on eyes, practice on regular blood check-up, eye examination and source of information were collected by interview technique using a structured questionnaire. Univariate and multiple logistic regression analysis were done to assess the association of awareness of eye examination with socio-demographic variables.
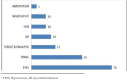
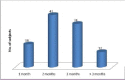
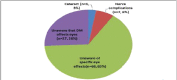
Results: Mean age of the study population was 56.7 years. About 93 people with diabetes (88.6%) tested their blood sugar at least once in every 3 months. About 80 people with diabetes (76.2%) were aware of at least one systemic complication of DM. Although 78 (74.3%) people with diabetes were aware that DM could affect the eyes, majority of this group (68, 87.2%) did not know the specific effects of DM on eyes. In this group, about 28(35.9%) people with diabetes were not aware of the reasons for eye effects, while others mentioned that persistent high blood sugar level (n=26, 33.3%), longer duration of DM (n=14, 17.9%) and lifestyle (n=10, 12.8%) were the reasons for the eye effects of DM. Only 31 (29.5%) of them knew that their eyes must be regularly examined. People with diabetes who had post-secondary and above (>10th standard) level of education had significantly higher awareness on examination of eye (Adjusted OR=19.63).
Conclusion: Although awareness of people with diabetes on systemic effects of DM was more, their awareness on specific eye effects and need for regular screening was low. Systematic efforts are required to increase awareness on eye effects and importance of regular screening in this population.
Keywords: Awareness; India; diabetes; eye effects; practice.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Assessment of awareness of diabetic retinopathy and utilization of eye care services among Turkish diabetic patients.Prim Care Diabetes. 2013 Dec;7(4):297-302. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2013.04.002. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Prim Care Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23639610
-
Knowledge of diabetes and diabetic retinopathy among rural populations in India, and the influence of knowledge of diabetic retinopathy on attitude and practice.Rural Remote Health. 2008 Jul-Sep;8(3):838. Epub 2008 Jul 24. Rural Remote Health. 2008. PMID: 18656993
-
Knowledge, attitude and practices on diabetes, hypertension and diabetic retinopathy and the factors that motivate screening for diabetes and diabetic retinopathy in a pyramidal model of eye health care.Rural Remote Health. 2018 Feb;18(1):4304. doi: 10.22605/RRH4304. Epub 2018 Feb 19. Rural Remote Health. 2018. PMID: 29458256
-
Sankara Nethralaya Diabetic Retinopathy Epidemiology and Molecular Genetic Study (SN--DREAMS III): study design and research methodology.BMC Ophthalmol. 2011 Mar 24;11:7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2415-11-7. BMC Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 21435202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The worldwide trend in diabetes awareness, treatment, and control from 1985 to 2022: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 233 population-representative studies.Front Public Health. 2024 May 17;12:1305304. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1305304. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38827607 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Awareness of Diabetic Retinopathy Among Diabetic Patients in King Khalid Eye Specialist Hospital, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.Cureus. 2022 Oct 19;14(10):e30458. doi: 10.7759/cureus.30458. eCollection 2022 Oct. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36407145 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes-Related Knowledge and Preventative Practices Among Government Employees with Diabetes in Kuwait.Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2017 Nov;17(4):e444-e451. doi: 10.18295/squmj.2017.17.04.011. Epub 2018 Jan 10. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2017. Retraction in: Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2018 May;18(2):e254. doi: 10.18295/SQUMJ.2018.18.02.028. PMID: 29372087 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Awareness of Diabetic Retinopathy Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Primary Healthcare Centers in Madinah, Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2023 Nov 30;15(11):e49718. doi: 10.7759/cureus.49718. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38033448 Free PMC article.
-
Updates on communicable and non-communicable diseases in LMICs.Afr Health Sci. 2016 Mar;16(1):i-iv. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v16i1.. Afr Health Sci. 2016. PMID: 27358652 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Awareness of cataract and glaucoma in two rural districts of Telangana, India.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022 Mar;70(3):982-987. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_977_21. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35225556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yam J, Kwok A. Update on the treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Hong Kong Med J. 2007;13:46–60. - PubMed
-
- Namperumalsamy P, Kim R, Kaliaperumal K, Sekar A, Karthika A, Nirmalan PK. A pilot study on awareness ofdiabetic retinopathy among non-medical persons in South India. The challenge for eye care programmes in the region. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2004;52:247–251. - PubMed
-
- Rani P, Raman R, Agarwal S, Paul PG, Uthra S, Margabandhu G, et al. Diabetic retinopathy screening model for rural population: awarenessand screening methodology. Rural and Remote Health. 2005;5:350–355. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
