Imaging in pulmonary hydatid cysts
- PMID: 27358685
- PMCID: PMC4919757
- DOI: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i6.581
Imaging in pulmonary hydatid cysts
Abstract
Hydatid disease is a zoonosis that can involve almost any organ in the human body. After the liver, the lungs are the most common site for hydatid disease in adults. Imaging plays a pivotal role in the diagnosis of the disease, as clinical features are often nonspecific. Classical radiological signs of pulmonary hydatid cysts have been described in the literature, aiding in the diagnosis of the disease. However, complicated hydatid cysts can prove to be a diagnostic challenge at times due to their atypical imaging features. Radiography is the initial imaging modality. Computed tomography can provide a specific diagnosis in complicated cases. Ultrasound is particularly useful in peripheral lung lesions. The role of magnetic resonance imaging largely remains unexplored.
Keywords: Computed tomography; Cyst; Hydatid; Pulmonary; Radiography.
Figures
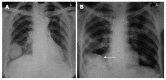
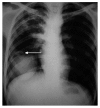
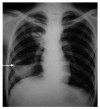
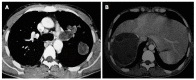
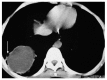
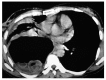
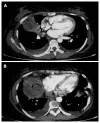
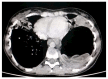
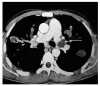
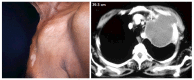
References
-
- Beggs I. The radiology of hydatid disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1985;145:639–648. - PubMed
-
- Lewall DB. Hydatid disease: biology, pathology, imaging and classification. Clin Radiol. 1998;53:863–874. - PubMed
-
- Aletras H. Symbas PN: Hydatid disease of the lung. In: Shields TW, LoCicero J, Ponn RB (eds.), General Thoracic Surgery, 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wil-kins; 2000: 1113-1122
-
- Milicevic M. Hydatid disease. In: Blugmart LH, editor. Surgery of the liver and biliary tract. 2nd ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Living-stone; 1994: 1121-1150 In: Blugmart LH, editor.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

