The Association Between Psychiatric Disorders and Telomere Length: A Meta-Analysis Involving 14,827 Persons
- PMID: 27359174
- PMCID: PMC5003712
- DOI: 10.1097/PSY.0000000000000356
The Association Between Psychiatric Disorders and Telomere Length: A Meta-Analysis Involving 14,827 Persons
Erratum in
-
The Association Between Psychiatric Disorders and Telomere Length: A Meta-Analysis Involving 14,827 Persons: Erratum.Psychosom Med. 2020 Jul/Aug;82(6):631. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0000000000000831. Psychosom Med. 2020. PMID: 32618906 No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: This study examined the relationship between leukocyte telomere length (LTL), a marker of cell aging, and psychiatric disorders in adults compared with controls using meta-analytic methods.
Methods: Data were abstracted from studies examining the relationship between LTL and adult psychiatric disorders. In addition to an overall estimate of effect size, subgroup analyses and meta-regression were performed to examine whether covariates (including psychiatric diagnoses) moderated the estimate.
Results: A significant overall effect size showing LTL shortening was found across all psychiatric disorders (Hedge g = -0.50, p < .001). Subgroup analyses did not demonstrate significant differences in effect size based on individual covariates (psychiatric disorder, sex, age, or assay method). The meta-regression indicated that although type of disorder and, likely, age moderate the overall effect size, the heterogeneity between studies could not be explained by a model that included these variables as well as sex and assay method. Although not significantly different, posttraumatic stress disorder, anxiety disorders, and depressive disorders had comparatively larger effect sizes (-1.27, -0.53, and -0.55), and psychotic and bipolar disorders had comparatively smaller ones (-0.23 and -0.26).
Conclusions: We observed a robust effect size of LTL shortening for psychiatric disorders as a whole compared with controls. The results were less straightforward regarding relative differences in the strength of this association by specific disorder. Future studies should focus on mechanisms explaining accelerated cell aging with psychiatric illness, defining directions (if any) of causality and elucidating possible differences in this association between disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of InterestDrs. Darrow, Lindqvist, Penninx, Delucchi, Wolkowitz and Mathews and Ms. Verhoeven and Ms. Révész report no financial relationships with commercial interests.
Figures
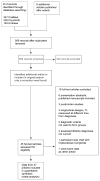
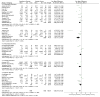

Comment in
-
Psychiatric Disorders, Morbidity, and Mortality: Tracing Mechanistic Pathways to Accelerated Aging.Psychosom Med. 2016 Sep;78(7):772-5. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0000000000000373. Psychosom Med. 2016. PMID: 27428860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Viron MJ, Stern TA. The impact of serious mental illness on health and healthcare. Psychosomatics. 2010;51(6):458–465. - PubMed
-
- D’Mello MJ, Ross SA, Briel M, Anand SS, Gerstein H, Pare G. Association between shortened leukocyte telomere length and cardiometabolic outcomes: systematic review and meta-analysis. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2015;8(1):82–90. - PubMed
-
- Cuijpers P, Vogelzangs N, Twisk J, Kleiboer A, Li J, Penninx BW. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Excess Mortality in Depression in the General Community Versus Patients With Specific Illnesses. American Journal of Psychiatry. 2014;171(4):453–462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

