mTOR Inhibition Suppresses Posttransplant Alloantibody Production Through Direct Inhibition of Alloprimed B Cells and Sparing of CD8+ Antibody-Suppressing T cells
- PMID: 27362313
- PMCID: PMC4992451
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001291
mTOR Inhibition Suppresses Posttransplant Alloantibody Production Through Direct Inhibition of Alloprimed B Cells and Sparing of CD8+ Antibody-Suppressing T cells
Abstract
Background: De novo alloantibodies (donor-specific antibody) contribute to antibody-mediated rejection and poor long-term graft survival. Because the development of donor-specific antibody is associated with early graft loss of cell transplants and reduced long-term survival of solid organ transplants, we hypothesized that conventional immunosuppressives, calcineurin inhibitors (CNi), and mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors (mTORi), may not be as effective for suppression of humoral alloimmunity as for cell-mediated immunity.
Methods: Wild-type or CD8-depleted mice were transplanted with allogeneic hepatocytes. Recipients were treated with mTORi and/or CNi and serially monitored for alloantibody and graft survival. The direct effect of mTORi and CNi on alloprimed B cell function was investigated in Rag1 mice adoptively transferred with alloprimed IgG1 B cells. The efficacy of mTORi and/or CNi to suppress CD8-mediated cytotoxicity of IgG1 B cells was evaluated in in vitro and in vivo cytotoxicity assays.
Results: Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors, but not CNi, reduced alloantibody production in transplant recipients, directly suppressed alloantibody production by alloprimed IgG1 B cells and delayed graft rejection in both low and high alloantibody producers. Combination treatment with mTORi and CNi resulted in loss of the inhibitory effect observed for mTORi monotherapy in part due to CNi suppression of CD8 T cells which downregulate alloantibody production (CD8 TAb-supp cells).
Conclusions: Our data support that mTORi is a potent inhibitor of humoral immunity through suppression of alloprimed B cells and preservation of CD8 TAb-supp cells. In contrast, alloantibody is readily detected in CNi-treated recipients because CNi does not suppress alloprimed B cells and interferes with downregulatory CD8 TAb-supp cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
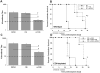
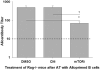



Similar articles
-
Antibody-suppressor CD8+ T Cells Require CXCR5.Transplantation. 2019 Sep;103(9):1809-1820. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002683. Transplantation. 2019. PMID: 30830040 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR5 + CD8 + T Cell-mediated Suppression of Humoral Alloimmunity and AMR in Mice Is Optimized With mTOR and Impaired With Calcineurin Inhibition.Transplantation. 2024 Mar 1;108(3):679-692. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000004828. Epub 2023 Oct 24. Transplantation. 2024. PMID: 37872660 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-Suppressor CXCR5+CD8+ T Cells Are More Potent Regulators of Humoral Alloimmunity after Kidney Transplant in Mice Compared to CD4+ Regulatory T Cells.J Immunol. 2024 May 1;212(9):1504-1518. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300289. J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38517294 Free PMC article.
-
Conversion From Calcineurin to Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Inhibitors in Liver Transplantation: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Transplantation. 2016 Mar;100(3):621-9. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001006. Transplantation. 2016. PMID: 26636736 Review.
-
Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Inhibitors Combined With Calcineurin Inhibitors as Initial Immunosuppression in Renal Transplantation: A Meta-analysis.Transplantation. 2019 Oct;103(10):2031-2056. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002769. Transplantation. 2019. PMID: 31343574
Cited by
-
Activation of the mTOR signaling pathway is required for asthma onset.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 3;7(1):4532. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04826-y. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28674387 Free PMC article.
-
B cell reconstitution following alemtuzumab induction under a belatacept-based maintenance regimen.Am J Transplant. 2020 Mar;20(3):653-662. doi: 10.1111/ajt.15639. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Am J Transplant. 2020. PMID: 31596034 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of immunosuppressants on tumor pulmonary metastasis: new insight into transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Biol Med. 2024 Dec 24;21(11):1033-49. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2024.0267. Cancer Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39718153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapamycin attenuates Tc1 and Tc17 cell responses in cigarette smoke-induced emphysema in mice.Inflamm Res. 2019 Nov;68(11):957-968. doi: 10.1007/s00011-019-01278-0. Epub 2019 Aug 29. Inflamm Res. 2019. PMID: 31468083
-
Antibody-suppressor CD8+ T Cells Require CXCR5.Transplantation. 2019 Sep;103(9):1809-1820. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002683. Transplantation. 2019. PMID: 30830040 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Einecke G, Sis B, Reeve J, et al. Antibody-mediated microcirculation injury is the major cause of late kidney transplant failure. Am J Transplant. 2009;9(11):2520–2531. - PubMed
-
- Sellares J, de Freitas DG, Mengel M, et al. Understanding the causes of kidney transplant failure: the dominant role of antibody-mediated rejection and nonadherence. Am J Transplant. 2012;12(2):388–399. - PubMed
-
- Gaston RS, Cecka JM, Kasiske BL, et al. Evidence for antibody-mediated injury as a major determinant of late kidney allograft failure. Transplantation. 2010;90(1):68–74. - PubMed
-
- Walker JP, Bumgardner GL. Hepatocyte immunology and transplantation: current status and future potential. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2005;10:67–76.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

