Tubular epithelial cells in renal clear cell carcinoma express high RIPK1/3 and show increased susceptibility to TNF receptor 1-induced necroptosis
- PMID: 27362805
- PMCID: PMC5108336
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2016.184
Tubular epithelial cells in renal clear cell carcinoma express high RIPK1/3 and show increased susceptibility to TNF receptor 1-induced necroptosis
Abstract
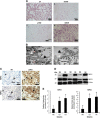
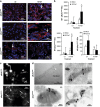
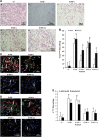
We previously reported that renal clear cell carcinoma cells (RCC) express both tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)-1 and -2, but that, in organ culture, a TNF mutein that only engages TNFR1, but not TNFR2, causes extensive cell death. Some RCC died by apoptosis based on detection of cleaved caspase 3 in a minority TUNEL-positive cells but the mechanism of death in the remaining cells was unexplained. Here, we underpin the mechanism of TNFR1-induced cell death in the majority of TUNEL-positive RCC cells, and show that they die by necroptosis. Malignant cells in high-grade tumors displayed threefold to four fold higher expression of both receptor-interacting protein kinase (RIPK)1 and RIPK3 compared with non-tumor kidney tubular epithelium and low-grade tumors, but expression of both enzymes was induced in lower grade tumors in organ culture in response to TNFR1 stimulation. Furthermore, TNFR1 activation induced significant MLKL(Ser358) and Drp1(Ser616) phosphorylation, physical interactions in RCC between RIPK1-RIPK3 and RIPK3-phospho-MLKL(Ser358), and coincidence of phospho-MLKL(ser358) and phospho-Drp1(Ser616) at mitochondria in TUNEL-positive RCC. A caspase inhibitor only partially reduced the extent of cell death following TNFR1 engagement in RCC cells, whereas three inhibitors, each targeting a different step in the necroptotic pathway, were much more protective. Combined inhibition of caspases and necroptosis provided additive protection, implying that different subsets of cells respond differently to TNF-α, the majority dying by necroptosis. We conclude that most high-grade RCC cells express increased amounts of RIPK1 and RIPK3 and are poised to undergo necroptosis in response to TNFR1 signaling.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Protein-Bound Polysaccharides from Coriolus Versicolor Induce RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL-Mediated Necroptosis in ER-Positive Breast Cancer and Amelanotic Melanoma Cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2020 Jun 13;54(4):591-604. doi: 10.33594/000000242. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32531147
-
RIPK3 contributes to TNFR1-mediated RIPK1 kinase-dependent apoptosis in conditions of cIAP1/2 depletion or TAK1 kinase inhibition.Cell Death Differ. 2013 Oct;20(10):1381-92. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2013.94. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Cell Death Differ. 2013. PMID: 23892367 Free PMC article.
-
TNFR1- and TNFR2-mediated signaling pathways in human kidney are cell type-specific and differentially contribute to renal injury.FASEB J. 2005 Oct;19(12):1637-45. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-3841com. FASEB J. 2005. PMID: 16195372
-
The resurrection of RIP kinase 1 as an early cell death checkpoint regulator-a potential target for therapy in the necroptosis era.Exp Mol Med. 2022 Sep;54(9):1401-1411. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00847-4. Epub 2022 Sep 28. Exp Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36171264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RIPK1 in necroptosis and recent progress in related pharmaceutics.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 11;16:1480027. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1480027. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40007541 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A prognosis model for clear cell renal cell carcinoma based on four necroptosis-related genes.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 9;9:942991. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.942991. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36016998 Free PMC article.
-
Frontier knowledge and future directions of programmed cell death in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Mar 5;10(1):113. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01880-0. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 38443363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Anti-Proliferative Activity of Secondary Metabolite from the Marine Streptomyces sp. against Prostate Cancer Cells.Life (Basel). 2021 Dec 16;11(12):1414. doi: 10.3390/life11121414. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34947945 Free PMC article.
-
Cell death-related molecules and biomarkers for renal cell carcinoma targeted therapy.Cancer Cell Int. 2019 Aug 23;19:221. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0939-2. eCollection 2019. Cancer Cell Int. 2019. PMID: 31462894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research trends, hot spots and prospects for necroptosis in the field of neuroscience.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Aug;16(8):1628-1637. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.303032. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 33433494 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Flanigan RC, Salmon SE, Blumenstein BA, Bearman SI, Roy V, McGrath PC et al. Nephrectomy followed by interferon alfa-2b compared with interferon alfa-2b alone for metastatic renal-cell cancer. N Engl J Med 2001; 345: 1655–1659. - PubMed
-
- Vandenabeele P, Declercq W, Van Herreweghe F, Vanden Berghe T. The role of the kinases RIP1 and RIP3 in TNF-induced necrosis. Sci Signal 2010; 3: re4. - PubMed
-
- Hu X, Han W, Li L. Targeting the weak point of cancer by induction of necroptosis. Autophagy 2007; 3: 490–492. - PubMed
-
- Al-Lamki RS, Bradley JR, Pober JS. Human organ culture as a tool for analyzing the response to tumor necrosis factor. Curr Trends Immunol 2011; 12: 49–66.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

