TC-N19, a novel dual inhibitor of EGFR and cMET, efficiently overcomes EGFR-TKI resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- PMID: 27362807
- PMCID: PMC5108342
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2016.192
TC-N19, a novel dual inhibitor of EGFR and cMET, efficiently overcomes EGFR-TKI resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer cells
Abstract
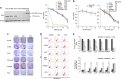
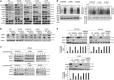
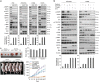
Epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) show a clinical benefit when used to treat patients with EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), but this treatment unfortunately fails in patients with TKI-resistant tumors. We here provide evidence that TC-N19 (N19), a novel dual inhibitor of EGFR and cMET, efficiently overcomes the EGFR-TKI resistance in EGFR-mutated NSCLC cells via simultaneous degradation of both proteins by ubiquitin proteasomes. Comparison with HSP90 inhibitor treatment and knockdown of EGFR and cMET by small hairpin RNAs reveal that the reduction of EGFR and cMET expression by N19 is responsible for overcoming the intrinsic TKI resistance mediated by paxillin (PXN) in high PXN-expressing cells, PXN-overexpressing PC9 cells (PC9-PXN), the EGFR-T790M-mediated TKI resistance in H1975 and CL97 cells, and the acquired resistance to gefitinib in gefitinib-resistant PC9 cells (PC9GR). Annexin V-PI staining assay showed that the induction of apoptosis in NSCLC cells by N19 depended on the reduction in levels of both proteins. Xenograft tumor formation in nude mice induced by a PC9-PXN-stable clone and by PC9GR cells was nearly completely suppressed by N19 treatment, with no changes in animal body weight. MTT assays of normal lung cells and reticulocytes showed no cytotoxicity responses to N19. In summary, N19 may act as a novel dual inhibitor of EGFR and cMET that induces apoptosis in TKI-resistant EGFR-mutated NSCLC cells and suppresses xenograft tumor formation. We suggest that N19 may be a potential new-generation TKI or HSP90 inhibitor used for treatment of NSCLC patients who show resistance to current TKI-targeting therapies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Novel Bispecific Antibody Targeting EGFR and cMet Is Effective against EGFR Inhibitor-Resistant Lung Tumors.Cancer Res. 2016 Jul 1;76(13):3942-53. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2833. Epub 2016 May 23. Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27216193
-
Butein, a novel dual inhibitor of MET and EGFR, overcomes gefitinib-resistant lung cancer growth.Mol Carcinog. 2015 Apr;54(4):322-31. doi: 10.1002/mc.22191. Epub 2014 Jun 29. Mol Carcinog. 2015. PMID: 24974831
-
Targeting Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Inducing Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Degradation via Methionine 790 Oxidation.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016 Feb 10;24(5):263-79. doi: 10.1089/ars.2015.6420. Epub 2015 Dec 14. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016. PMID: 26528827 Free PMC article.
-
Current mechanism of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors and updated therapy strategies in human nonsmall cell lung cancer.J Cancer Res Ther. 2016 Dec;12(Supplement):C131-C137. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.200613. J Cancer Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 28230005 Review.
-
The role of cMet in non-small cell lung cancer resistant to EGFR-inhibitors: did we really find the target?Curr Drug Targets. 2014;15(14):1284-92. doi: 10.2174/138945011514141216092739. Curr Drug Targets. 2014. PMID: 25511614 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic-Based Identification of the Immuno-Oncogenic Signature of Cholangiocarcinoma for HLC-018 Multi-Target Therapy Exploration.Cells. 2021 Oct 25;10(11):2873. doi: 10.3390/cells10112873. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831096 Free PMC article.
-
In-Silico Evaluation of Genetic Alterations in Ovarian Carcinoma and Therapeutic Efficacy of NSC777201, as a Novel Multi-Target Agent for TTK, NEK2, and CDK1.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 31;22(11):5895. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115895. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34072728 Free PMC article.
-
Epitranscriptomics and epiproteomics in cancer drug resistance: therapeutic implications.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Sep 8;5(1):193. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00300-w. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 32900991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative Analysis of Membrane Proteome and MicroRNA Reveals Novel Lung Cancer Metastasis Biomarkers.Front Genet. 2020 Aug 28;11:1023. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.01023. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33005184 Free PMC article.
-
In-silico analysis of TMEM2 as a pancreatic adenocarcinoma and cancer-associated fibroblast biomarker, and functional characterization of NSC777201, for targeted drug development.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 15;14(6):3010-3035. doi: 10.62347/CHXD6134. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39005682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mok TS. Personalized medicine in lung cancer: what we need to know. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2011; 8: 661–668. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Moran T, Queralt C, Porta R, Cardenal F, Camps C et al. Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2009; 361: 958–967. - PubMed
-
- Tan CS, Gilligan D, Pacey S. Treatment approaches for EGFR-inhibitor-resistant patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol 2015; 16: e447–e459. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

