miRNA-205 targets VEGFA and FGF2 and regulates resistance to chemotherapeutics in breast cancer
- PMID: 27362808
- PMCID: PMC5108343
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2016.194
miRNA-205 targets VEGFA and FGF2 and regulates resistance to chemotherapeutics in breast cancer
Abstract
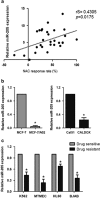
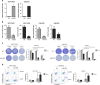
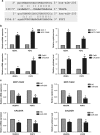
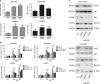
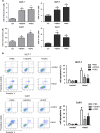
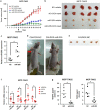
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have critical roles in regulating cancer cell survival, proliferation and sensitivity to chemotherapy. The potential application of using miRNAs to predict chemotherapeutic response to cancer treatment is highly promising. However, the underlying mechanisms of chemotherapy response control by miRNAs remain to be fully identified and their prognostic value has not been fully evaluated. Here we show a strong correlation between miR-205 expression and chemosensitivtiy to TAC (docetaxol, doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide), a widely-used neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) regimen, for breast cancer patients. High level of miR-205 predicted better response to TAC regimen NAC in breast cancer patients. We found miR-205 downregulated in both MCF-7/A02 and CALDOX cells, two drug-resistant derivatives of MCF-7 and Cal51 cells, and its ectopic expression led to an increase in apoptosis resensitization of both drug-resistant cell lines to doxorubicin and taxol. We further show that miR-205 directly binds VEGFA and FGF2 mRNA 3'-UTRs and confirm that miR-205 levels are negatively correlated with VEGFA and FGF2 mRNA expression in breast cancer patients. Adding VEGFA and FGF2 exogenously to chemosensitive breast cancer cells and chemoresistant cells with miR-205 overexpression led to drug resistance. Consistently, low VEGFA and FGF2 expression correlated with better response to NAC in breast cancer patients. In addition, inhibition of tumor growth and resensitization to doxorubicin were also observed in mouse tumor xenografts from cells overexpressing miR-205. Taken together, our data suggest that miR-205 enhances chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells to TAC chemotherapy by suppressing both VEGFA and FGF2, leading to evasion of apoptosis. MiR-205 may serve as a predictive biomarker and a potential therapeutic target in breast cancer treatment.
Figures




References
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 2016; 66: 115–132. - PubMed
-
- Dieras V, Fumoleau P, Romieu G, Tubiana-Hulin M, Namer M, Mauriac L et al. Randomized parallel study of doxorubicin plus paclitaxel and doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide as neoadjuvant treatment of patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 4958–4965. - PubMed
-
- Nowak AK, Wilcken NR, Stockler MR, Hamilton A, Ghersi D. Systematic review of taxane-containing versus non-taxane-containing regimens for adjuvant and neoadjuvant treatment of early breast cancer. Lancet Oncol 2004; 5: 372–380. - PubMed
-
- Bonnefoi H, Litiere S, Piccart M, MacGrogan G, Fumoleau P, Brain E et al. Pathological complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy is an independent predictive factor irrespective of simplified breast cancer intrinsic subtypes: a landmark and two-step approach analyses from the EORTC 10994/BIG 1-00 phase III trial. Ann Oncol 2014; 25: 1128–1136. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

