Antimitotic activity of DY131 and the estrogen-related receptor beta 2 (ERRβ2) splice variant in breast cancer
- PMID: 27363015
- PMCID: PMC5216935
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9719
Antimitotic activity of DY131 and the estrogen-related receptor beta 2 (ERRβ2) splice variant in breast cancer
Abstract
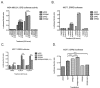
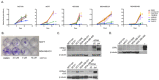
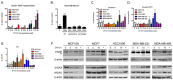
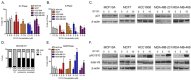
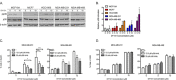
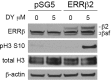
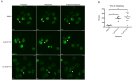
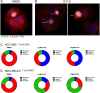
Breast cancer remains a leading cause of cancer-related death in women, and triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) lacks clinically actionable therapeutic targets. Death in mitosis is a tumor suppressive mechanism that occurs in cancer cells experiencing a defective M phase. The orphan estrogen-related receptor beta (ERRβ) is a key reprogramming factor in murine embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells. In primates, ERRβ is alternatively spliced to produce several receptor isoforms. In cellular models of glioblastoma, short form (ERRβsf) and beta2 (ERRβ2) splice variants differentially regulate cell cycle progression in response to the synthetic agonist DY131, with ERRβ2 driving arrest in G2/M.The goals of the present study are to determine the cellular function(s) of ligand-activated ERRβ splice variants in breast cancer and evaluate the potential of DY131 to serve as an antimitotic agent, particularly in TNBC. DY131 inhibits growth in a diverse panel of breast cancer cell lines, causing cell death that involves the p38 stress kinase pathway and a bimodal cell cycle arrest. ERRβ2 facilitates the block in G2/M, and DY131 delays progression from prophase to anaphase. Finally, ERRβ2 localizes to centrosomes and DY131 causes mitotic spindle defects. Targeting ERRβ2 may therefore be a promising therapeutic strategy in breast cancer.
Keywords: ERRbeta; ESRRB; cell death; mitosis; p38 MAPK.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- DeSantis C, Siegel R, Bandi P, Jemal A. Breast cancer statistics, 2011. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:409–418. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Kohler BA, Sherman RL, Howlader N, Jemal A, Ryerson AB, Henry KA, Boscoe FP, Cronin KA, Lake A, Noone AM, Henley SJ, Eheman CR, Anderson RN, Penberthy L. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975-2011, featuring incidence of breast cancer subtypes by race/ethnicity, poverty, and state. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015;107:djv048. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Abrams JM, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, El-Deiry WS, Fulda S, Gottlieb E, Green DR, Hengartner MO, et al. Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: Recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death 2012. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19:107–120. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

