Docosahexaenoic acid suppresses breast cancer cell metastasis by targeting matrix-metalloproteinases
- PMID: 27363023
- PMCID: PMC5226561
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.10266
Docosahexaenoic acid suppresses breast cancer cell metastasis by targeting matrix-metalloproteinases
Abstract
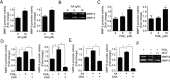
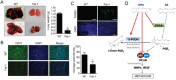
Breast cancer is one of the most prevalent cancers in women, and nearly half of breast cancer patients develop distant metastatic disease after therapy. Despite the significant advances that have been achieved in understanding breast cancer metastasis in the past decades, metastatic cancer is still hard to cure. Here, we demonstrated an anti-cancer mechanism of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) that suppressed lung metastasis in breast cancer. DHA could inhibit proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells in vitro, and this was mainly through blocking Cox-2-PGE2-NF-κB-MMPs cascades. DHA treatment significantly decreased Cox-2 and NF-κB expression as well as nuclear translocation of NF-κB in MDA-MB-231 cells. In addition, DHA also reduced NF-κB binding to DNA which may lead to inactivation of MMPs. Moreover, in vivo studies using Fat-1 transgenic mice showed remarkable decrease of tumor growth and metastasis to EO771 cells to lung in DHA-rich environment. In conclusion, DHA attenuated breast cancer progression and lung metastasis in part through suppressing MMPs, and these findings suggest chemoprevention and potential therapeutic strategy to overcome malignant breast cancer.
Keywords: DHA; MMP; breast cancer; omega-3 PUFA.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors of this paper declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Curcumol Suppresses Breast Cancer Cell Metastasis by Inhibiting MMP-9 Via JNK1/2 and Akt-Dependent NF-κB Signaling Pathways.Integr Cancer Ther. 2016 Jun;15(2):216-25. doi: 10.1177/1534735416642865. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Integr Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 27125675 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression by docosahexaenoic acid mediated by heme oxygenase 1 in 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced MCF-7 human breast cancer cells.Arch Toxicol. 2013 May;87(5):857-69. doi: 10.1007/s00204-012-1003-3. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Arch Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23288142
-
Aromatic-turmerone attenuates invasion and expression of MMP-9 and COX-2 through inhibition of NF-κB activation in TPA-induced breast cancer cells.J Cell Biochem. 2012 Dec;113(12):3653-62. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24238. J Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22740037
-
Cytoguardin: A Tryptophan Metabolite against Cancer Growth and Metastasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 26;22(9):4490. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094490. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33925793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of microRNAs regulating the expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in breast cancer development, progression, and metastasis.J Cell Physiol. 2019 May;234(5):5399-5412. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27445. Epub 2018 Nov 22. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30565667 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of the Expression of ELOVL5 and IGFBP6 Genes on the Metastatic Potential of Breast Cancer Cells.Front Genet. 2021 Jun 2;12:662843. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.662843. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34149804 Free PMC article.
-
Increased lipogenesis is critical for self-renewal and growth of breast cancer stem cells: Impact of omega-3 fatty acids.Stem Cells. 2021 Dec;39(12):1660-1670. doi: 10.1002/stem.3452. Epub 2021 Sep 17. Stem Cells. 2021. PMID: 34486791 Free PMC article.
-
Scutellaria barbata D. Don inhibits migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells via suppression of PI3K/AKT and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Dec;14(6):5527-5534. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5242. Epub 2017 Oct 2. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 29285087 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of the Relative Efficacy of Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid for Anti-Cancer Effects in Human Breast Cancer Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Dec 4;18(12):2607. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122607. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29207553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymorphisms in matrix metalloproteinases 2, 3, and 8 increase recurrence and mortality risk by regulating enzyme activity in gastric adenocarcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Nov 20;8(62):105971-105983. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22516. eCollection 2017 Dec 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29285307 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- Ravdin PM, Cronin KA, Howlader N, Berg CD, Chlebowski RT, Feuer EJ, Edwards BK, Berry DA. The decrease in breast-cancer incidence in 2003 in the United States. The New England journal of medicine. 2007;356:1670–1674. - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Redmond C, Poisson R, Margolese R, Wolmark N, Wickerham L, Fisher E, Deutsch M, Caplan R, Pilch Y, Glass A, Shibata H, Lerner H, Terz J, Sidorovich L. Eight-year results of a randomized clinical trial comparing total mastectomy and lumpectomy with or without irradiation in the treatment of breast cancer. The New England journal of medicine. 1989;320:822–828. - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Anderson S, Fisher ER, Redmond C, Wickerham DL, Wolmark N, Mamounas EP, Deutsch M, Margolese R. Significance of ipsilateral breast tumour recurrence after lumpectomy. Lancet. 1991;338:327–331. - PubMed
-
- Veronesi U, Marubini E, Del Vecchio M, Manzari A, Andreola S, Greco M, Luini A, Merson M, Saccozzi R, Rilke F, Salvadori B. Local recurrences and distant metastases after conservative breast cancer treatments: partly independent events. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995;87:19–27. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

