The metabolome of [2-(14)C](-)-epicatechin in humans: implications for the assessment of efficacy, safety, and mechanisms of action of polyphenolic bioactives
- PMID: 27363516
- PMCID: PMC4929566
- DOI: 10.1038/srep29034
The metabolome of [2-(14)C](-)-epicatechin in humans: implications for the assessment of efficacy, safety, and mechanisms of action of polyphenolic bioactives
Abstract
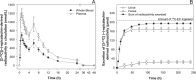
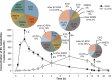
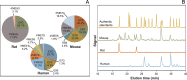
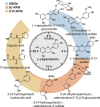
Diet is a major life style factor affecting human health, thus emphasizing the need for evidence-based dietary guidelines for primary disease prevention. While current recommendations promote intake of fruit and vegetables, we have limited understanding of plant-derived bioactive food constituents other than those representing the small number of essential nutrients and minerals. This limited understanding can be attributed to some extent to a lack of fundamental data describing the absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME) of bioactive compounds. Consequently, we selected the flavanol (-)-epicatechin (EC) as an example of a widely studied bioactive food constituent and investigated the ADME of [2-(14)C](-)-epicatechin (300 μCi, 60 mg) in humans (n = 8). We demonstrated that 82 ± 5% of ingested EC was absorbed. We also established pharmacokinetic profiles and identified and quantified >20 different metabolites. The gut microbiome proved to be a key driver of EC metabolism. Furthermore, we noted striking species-dependent differences in the metabolism of EC, an insight with significant consequences for investigating the mechanisms of action underlying the beneficial effects of EC. These differences need to be considered when assessing the safety of EC intake in humans. We also identified a potential biomarker for the objective assessment of EC intake that could help to strengthen epidemiological investigations.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01969994.
Conflict of interest statement
H.S. and J.I.O. are employed by Mars Inc., a company engaged in flavanol research and flavanol-related commercial activities. C.L.K., J.P.E.S., and A.C. have received an unrestricted research grant from Mars Inc. In addition, C.L.K. and A.C. have consulted for Mars, Inc. and other food companies and government agencies with an interest in health and nutrition, as well as in dietary bioactives, including flavanols and procyanidins.
Figures

References
-
- USDA and USDHHS. Dietary Guidelines for Americans. Ch. 4 (Washignton DC, 2010).
-
- IOM. Dietary Reference Intakes: The Essential Guide to Nutrient Requirements (eds. Otten J. J. Pitzi Hellwig J. & Meyers L. D. , Washignton DC, 2006).
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

