Towards Enhanced Performance Thin-film Composite Membranes via Surface Plasma Modification
- PMID: 27363670
- PMCID: PMC4929684
- DOI: 10.1038/srep29206
Towards Enhanced Performance Thin-film Composite Membranes via Surface Plasma Modification
Abstract
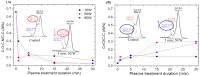
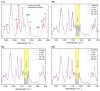
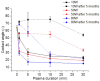
Advancing the design of thin-film composite membrane surfaces is one of the most promising pathways to deal with treating varying water qualities and increase their long-term stability and permeability. Although plasma technologies have been explored for surface modification of bulk micro and ultrafiltration membrane materials, the modification of thin film composite membranes is yet to be systematically investigated. Here, the performance of commercial thin-film composite desalination membranes has been significantly enhanced by rapid and facile, low pressure, argon plasma activation. Pressure driven water desalination tests showed that at low power density, flux was improved by 22% without compromising salt rejection. Various plasma durations and excitation powers have been systematically evaluated to assess the impact of plasma glow reactions on the physico-chemical properties of these materials associated with permeability. With increasing power density, plasma treatment enhanced the hydrophilicity of the surfaces, where water contact angles decreasing by 70% were strongly correlated with increased negative charge and smooth uniform surface morphology. These results highlight a versatile chemical modification technique for post-treatment of commercial membrane products that provides uniform morphology and chemically altered surface properties.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Plasma Modification and Synthesis of Membrane Materials-A Mechanistic Review.Membranes (Basel). 2018 Aug 3;8(3):56. doi: 10.3390/membranes8030056. Membranes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30081505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amine Enrichment of Thin-Film Composite Membranes via Low Pressure Plasma Polymerization for Antimicrobial Adhesion.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015 Jul 15;7(27):14644-53. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b01603. Epub 2015 Jul 1. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015. PMID: 26083007
-
Supramolecular-Based Regenerable Coating Layer of a Thin-Film Composite Nanofiltration Membrane for Simultaneously Enhanced Desalination and Antifouling Properties.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019 Jun 12;11(23):21137-21149. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b03761. Epub 2019 May 31. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019. PMID: 31119932
-
High performance thin-film composite forward osmosis membrane.Environ Sci Technol. 2010 May 15;44(10):3812-8. doi: 10.1021/es1002555. Environ Sci Technol. 2010. PMID: 20408540
-
Surface characterization of thin-film composite membranes using contact angle technique: Review of quantification strategies and applications.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2022 Jan;299:102524. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2021.102524. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2022. PMID: 34620491 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma Modification and Synthesis of Membrane Materials-A Mechanistic Review.Membranes (Basel). 2018 Aug 3;8(3):56. doi: 10.3390/membranes8030056. Membranes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30081505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies to Enhance the Membrane-Based Processing Performance for Fruit Juice Production: A Review.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Jul 20;13(7):679. doi: 10.3390/membranes13070679. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37505045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fouling in reverse osmosis membranes: monitoring, characterization, mitigation strategies and future directions.Heliyon. 2023 Mar 28;9(4):e14908. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14908. eCollection 2023 Apr. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37064488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advancements in Polyphenylsulfone Membrane Modification Methods for Separation Applications.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Feb 21;12(2):247. doi: 10.3390/membranes12020247. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35207168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Charge tunable thin-film composite membranes by gamma-ray triggered surface polymerization.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 30;7(1):4426. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04900-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28667264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu G.-R., Wang J.-N. & Li C.-J. In Desalination Vol. 328, 83–100 (2013).
-
- Kochkodan V., Johnson D. J. & Hilal N. Polymeric membranes: Surface modification for minimizing (bio)colloidal fouling. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 206, 116–140 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Lee K. P., Arnot T. C. & Mattia D. A review of reverse osmosis membrane materials for desalination development to date and future potential. Journal of Membrane Science 370, 1–22 (2011).
-
- Baker J. S. & Dudley L. Y. Biofouling in membrane systems — A review. Desalination 118, 81–89 (1998).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

