miR-4284 and miR-4484 as Putative Biomarkers for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
- PMID: 27365556
- PMCID: PMC4912653
miR-4284 and miR-4484 as Putative Biomarkers for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous small RNA, which can regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. MiRNA profiling has shown a great potential as novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. The present study was performed at the Nemazee Teaching Hospital (Shiraz, Iran) from 2011 to 2013. The aim of this study was to assess the deregulation of miRNAs profiles in DLBL against hyperplasic reactive lymph node as a normal. This could serve as a biomarker for DLBL. The miRCURY LNA™ microarray was used on the total RNA, which was extracted from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue of 24 de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients and 14 normal lymph nodes. The greatest changes were detected in miR-4284 and miR-4484 level in patient's lymphoma samples. These miRNAs can act as a diagnostic biomarker for DLBL.
Keywords: Diffuse; Large B-Cell; Lymphoma; MicroRNAs; Microarray Analysis.
Figures
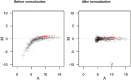
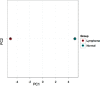

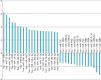
References
-
- Macfarlane LA, Murphy PR. MicroRNA:Biogenesis, Function and Role in Cancer. Curr Genomics. 2010;11:537–61. doi: 10.2174/138920210793175895. [ PMC Free Article] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pillai RS. MicroRNA function:multiple mechanisms for a tiny RNA? RNA. 2005;11:1753–61. doi: 10.1261/rna.2248605. [ PMC Free Article] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rai D, Karanti S, Jung I, Dahia PL, Aguiar RC. Coordinated expression of microRNA-155 and predicted target genes in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2008;181:8–15. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergencyto.2007.10.008. [ PMC Free Article] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
