Transformation of eutectic emulsion to nanosuspension fabricating with solvent evaporation and ultrasonication technique
- PMID: 27366064
- PMCID: PMC4914070
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S108355
Transformation of eutectic emulsion to nanosuspension fabricating with solvent evaporation and ultrasonication technique
Abstract
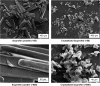
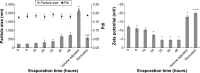
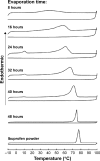
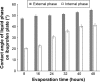
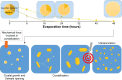
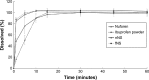
Eutectic solvent can solubilize high amount of some therapeutic compounds. Volatile eutectic solvent is interesting to be used as solvent in the preparation of nanosuspension with emulsion solvent evaporation technique. The mechanism of transformation from the eutectic emulsion to nanosuspension was investigated in this study. The 30% w/w ibuprofen eutectic solution was used as the internal phase, and the external phase is composed of Tween 80 as emulsifier. Ibuprofen nanosuspension was prepared by eutectic emulsion solvent evaporating method followed with ultrasonication. During evaporation process, the ibuprofen concentration in emulsion droplets was increased leading to a drug supersaturation but did not immediately recrystallize because of low glass transition temperature (T g) of ibuprofen. The contact angle of the internal phase on ibuprofen was apparently lower than that of the external phase at all times of evaporation, indicating that the ibuprofen crystals were preferentially wetted by the internal phase than the external phase. From calculated dewetting value ibuprofen crystallization occurred in the droplet. Crystallization of the drug was initiated with external mechanical force, and the particle size of the drug was larger due to Ostwald ripening. Cavitation force from ultrasonication minimized the ibuprofen crystals to the nanoscale. Particle size and zeta potential of formulated ibuprofen nanosuspension were 330.87±51.49 nm and -31.1±1.6 mV, respectively, and exhibited a fast dissolution. Therefore, the combination of eutectic emulsion solvent evaporation method with ultrasonication was favorable for fabricating an ibuprofen nanosuspension, and the transformation mechanism was attained successfully.
Keywords: emulsion solvent evaporation; eutectic; ibuprofen; nanosuspension; ultrasonication.
Figures
References
-
- Verma S, Gokhale R, Burgess DJ. A comparative study of top-down and bottom-up approaches for the preparation of micro/nanosuspensions. Int J Pharm. 2009;380:216–222. - PubMed
-
- Möschwitzer JP. Drug nanocrystals in the commercial pharmaceutical development process. Int J Pharm. 2012;453:142–156. - PubMed
-
- Chan HK, Kwok PC. Production methods for nanodrug particles using the bottom-up approach. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63:406–416. - PubMed
-
- Chingunpituk J. Nanosuspension technology for drug delivery. Walailak J Sci Tech. 2007;4:139–153.
-
- Lakshmi P, Kumar G. Nano-suspension technology: a review. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2010;2:35–40.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

