Toxicity evaluation of crankcase oil in rats
- PMID: 27366138
- PMCID: PMC4928016
Toxicity evaluation of crankcase oil in rats
Abstract
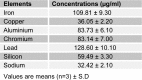
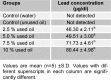
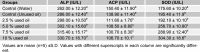
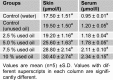
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of crankcase oil on the cellular and functional integrity of rat skin. Thirty (30) rats were randomly grouped into six viz groups A-F. Group A (base-line control) received 2 ml of distilled water. 2.5 %, 5.0 %, 7.5 %, and 10.0 % v/v of the crankcase oil were prepared using unused oil as solvent and 2 ml of the concentrations were topically administered to groups C-F respectively for seven consecutive days. Group B served as positive control and received 2 ml of the unused oil. The rats were sacrificed 24 hours after the last administration, and blood and part of the skin were collected. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP), acid phosphatase (ACP), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and malondialdehyde level in the blood and skin samples collected were evaluated. Elemental analysis of the crankcase oil was also carried out. The result revealed high lead, iron and chromium levels. Blood lead concentration of rats was significantly (P<0.05) high after seven days of administration. ALP level in skin and serum increased significantly (P<0.05) with the concentration of crankcase oil. There was a significant decrease (P<0.05) in skin ACP activity while it increased significantly (P<0.05) in the serum. Similar results were observed in the SOD levels of the serum and the skin. The level increased significantly (P<0.05) in groups D-F when compared with controls. The MDA concentration of both serum and skin were significantly (P<0.05) elevated. This suggests toxic potential of used lubricating oil and its potential predisposition to cancer.
Keywords: cancer; crankcase oil; malondialdehyde; superoxide dismutase.
Figures

References
-
- Akanji MA, Olagoke OA, Oloyede OB. Effect of chronic consumption of metabiosulphate on the integrity of rat kidney cellular system. Toxicology. 1993;81:173–179. - PubMed
-
- Anoliefo GO, Edegbai BO. Effect of spent engine oil as a soil contaminant on the growth of two eggplant species;Solanum melongena L. and S. incanum. J Agric Forestry Fish. 2000;1:21–25.
-
- ATSDR (Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry) Toxicological Profile for mineral base crankcase oil. Atlanta, GA: Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service Press,; 1997.
-
- Carmichael PL, Jacob J, Grimmer G, Phillips DH. Analysis of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon content of petrol and diesel engine lubricating oils and determination of DNA adducts in topically treated mice by 32P-postlabelling. Carcinogenesis. 1990;11:2025–2032. - PubMed
-
- Carmichael PL, Ni Shé M, Hewer A, Jacob J, Grimmer G, Phillips DH. DNA adduct formation in mice following treatment with used engine oil and identification of some of the major adducts by 32P-postlabelling. Cancer Lett. 1992;64:137–144. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
