Protective effect of curcumin on experimentally induced arthritic rats: detailed histopathological study of the joints and white blood cell count
- PMID: 27366139
- PMCID: PMC4928023
Protective effect of curcumin on experimentally induced arthritic rats: detailed histopathological study of the joints and white blood cell count
Abstract
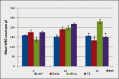
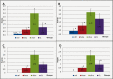
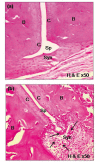
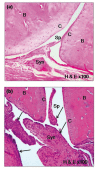
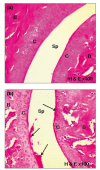
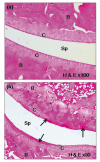
Curcuma longa (turmeric) rhizomes contains curcumin, an active compound which possesses anti-inflammatory effects. Collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) is an accepted experimental animal model of rheumatoid arthritis. The present study aimed to observe the histological changes in the joints of experimental arthritic rats treated with curcumin. Twenty four male Sprague-Dawley (approximately 7 weeks-old) rats were randomly divided into four groups. Three groups were immunized with 150 µg collagen. All rats with established CIA, with arthritis scores exceeding 1, were orally treated with betamethasone (0.5 mg/ml/kg body weight), curcumin (110 mg/ml/kg body weight) or olive oil (1.0 ml/kg body weight) daily, for two weeks. One remaining group was kept as normal control. Treatment with 110 mg/ml/kg curcumin showed significant mean differences in the average white blood cell (WBC) count (p<0.05), cell infiltration, bone and cartilage erosion scores (p<0.05) compared to the olive oil treated group. Pannus formation scores showed that curcumin supplementation successfully suppressed the pannus formation process that occurred in the articular cartilage of the CIA joints. The mean difference for histological scores for the curcumin group was insignificant compared to the betamethasone treated group. It is concluded that supplementation of curcumin has protective effect on the histopathological and degenerative changes in the joints of CIA rats which was at par with betamethasone.
Keywords: arthritis; collagen; curcumin; experimental; histopathology; inflammation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of Curcuma longa (turmeric) on collagen-induced arthritis: an anatomico-radiological study.Clin Ter. 2011;162(3):201-7. Clin Ter. 2011. PMID: 21717043
-
Crocin exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effects on type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats.Pharm Biol. 2018 Dec;56(1):209-216. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2018.1448874. Pharm Biol. 2018. PMID: 29540097 Free PMC article.
-
[Inhibition of cartilage destruction in collagen-induced arthritis by altered CII 263-272 peptide: experiment with rats].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006 Nov 21;86(43):3055-8. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17288836 Chinese.
-
NTP Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of Turmeric Oleoresin (CAS No. 8024-37-1) (Major Component 79%-85% Curcumin, CAS No. 458-37-7) in F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice (Feed Studies).Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 1993 Aug;427:1-275. Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 1993. PMID: 12616304
-
[Comparative study on dose-toxicity-effect of Tripterygium Glycosides Tablets and Tripterygium wilfordii Tablets on CIA model rats].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019 Aug;44(16):3502-3511. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190703.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31602915 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Diacetylcurcumin: Its Potential Antiarthritic Effect on a Freund's Complete Adjuvant-Induced Murine Model.Molecules. 2019 Jul 21;24(14):2643. doi: 10.3390/molecules24142643. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31330908 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin and Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate Ankle, Testis, and Ovary Deleterious Histological Changes in Arthritic Rats via Suppression of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation.Stem Cells Int. 2021 Nov 9;2021:3516834. doi: 10.1155/2021/3516834. eCollection 2021. Stem Cells Int. 2021. PMID: 34795765 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Curcumin with Iontophoretic Application on Paw Edema and Hematological Responses in Collagen-Induced Arthritis Rat Models.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Apr 9;2020:4606520. doi: 10.1155/2020/4606520. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32351596 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Curcumin Effectively Mitigate Freund's Adjuvant- induced Arthritis via their Anti-inflammatory and Gene Expression of COX-1, IL-6 and IL-4.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024;24(4):468-488. doi: 10.2174/1871530323666230223143011. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 36825726
-
Treatment of Psoriatic Arthritis With Acupuncture, Turmeric (Curcuma longa), Sarsaparilla (Smilax officinalis) and Vitamin D: A Case Report.J Chiropr Med. 2020 Sep;19(3):194-200. doi: 10.1016/j.jcm.2019.12.005. Epub 2020 Dec 15. J Chiropr Med. 2020. PMID: 33362443 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aggarwal BB, Kumar A, Aggarwal MS, Shishodia S. Curcumin derived from turmeric (Curcuma longa): A spice for all seasons. In: Preuss H, editor. Phytochemicals in cancer chemoprevention. New York: CRC Press; 2005. pp. 349–387.
-
- Antony S, Kuttan R, Kuttan G. Immunomodulatory activity of curcumin. Immunol Invest. 1999;28:291–303. - PubMed
-
- Arend WP. Cytokine imbalance in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: The role of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Sem Arthritis Rheum. 2001;30(Suppl 2):1–6. - PubMed
-
- Arthritis Foundation Malaysia. Rheumatoid arthritis. 2007. [2.5.2012]. Available from: http://www.afm.org.my/
-
- Brand DD, Latham KA, Rosloniec EF. Collagen-induced arthritis. Nature Protocols. 2007;2:1269–75. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
