Natural diversity of cellulases, xylanases, and chitinases in bacteria
- PMID: 27366206
- PMCID: PMC4928363
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-016-0538-6
Natural diversity of cellulases, xylanases, and chitinases in bacteria
Abstract
Background: Glycoside hydrolases (GH) targeting cellulose, xylan, and chitin are common in the bacterial genomes that have been sequenced. Little is known, however, about the architecture of multi-domain and multi-activity glycoside hydrolases. In these enzymes, combined catalytic domains act synergistically and thus display overall improved catalytic efficiency, making these proteins of high interest for the biofuel technology industry.
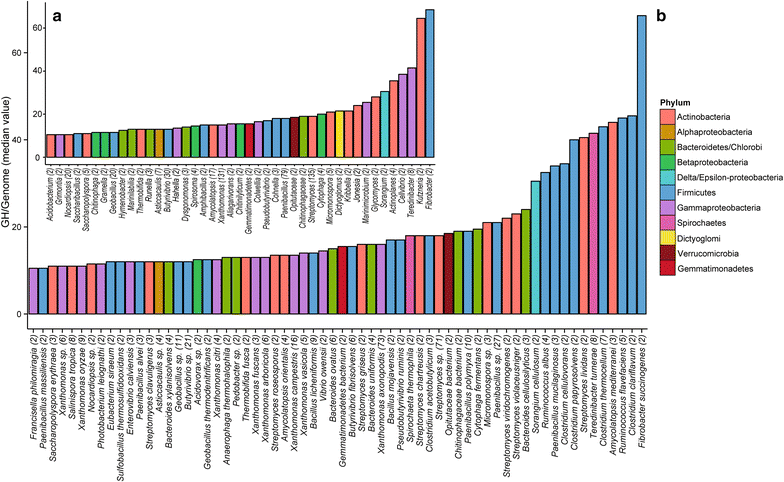
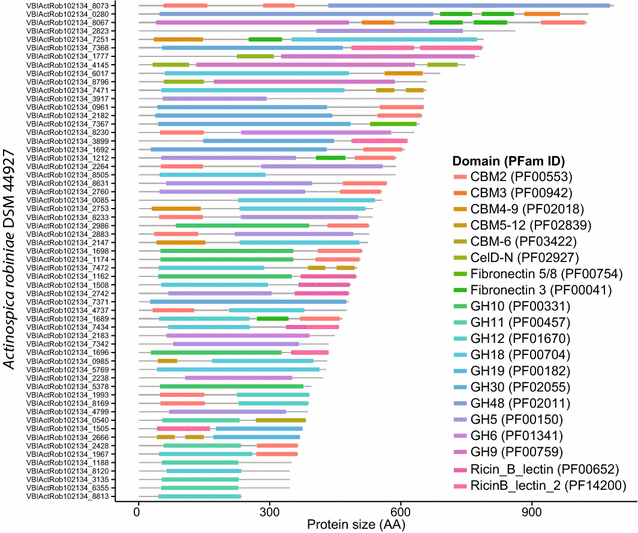
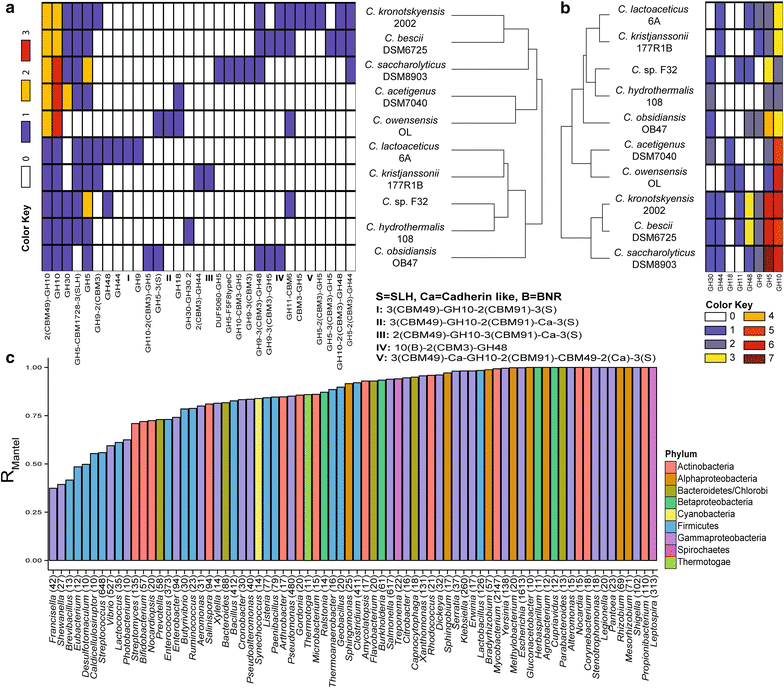
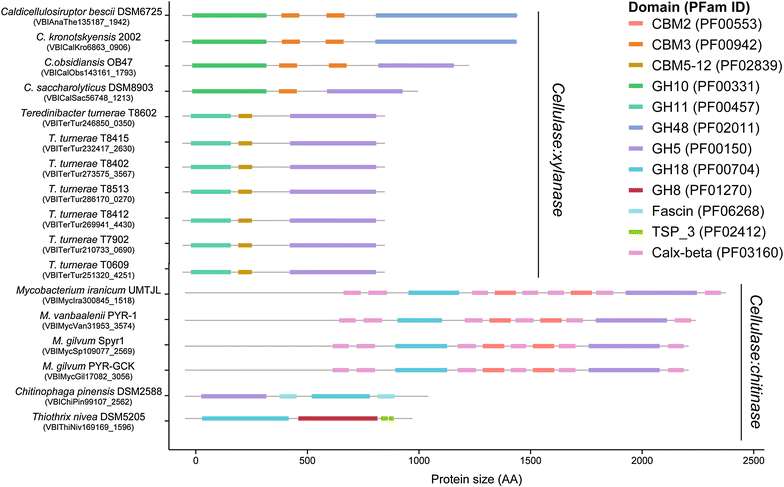
Results: Here, we identify the domain organization in 40,946 proteins targeting cellulose, xylan, and chitin derived from 11,953 sequenced bacterial genomes. These bacteria are known to be capable, or to have the potential, to degrade polysaccharides, or are newly identified potential degraders (e.g., Actinospica, Hamadaea, Cystobacter, and Microbispora). Most of the proteins we identified contain a single catalytic domain that is frequently associated with an accessory non-catalytic domain. Regarding multi-domain proteins, we found that many bacterial strains have unique GH protein architectures and that the overall protein organization is not conserved across most genera. We identified 217 multi-activity proteins with at least two GH domains for cellulose, xylan, and chitin. Of these proteins, 211 have GH domains targeting similar or associated substrates (i.e., cellulose and xylan), whereas only six proteins target both cellulose and chitin. Fifty-two percent of multi-activity GHs are hetero-GHs. Finally, GH6, -10, -44 and -48 domains were mostly C-terminal; GH9, -11, -12, and -18 were mostly N-terminal; and GH5 domains were either N- or C-terminal.
Conclusion: We identified 40,946 multi-domain/multi-activity proteins targeting cellulase, chitinase, and xylanase in bacterial genomes and proposed new candidate lineages and protein architectures for carbohydrate processing that may play a role in biofuel production.
Keywords: Biofuel; CAZy; Carbohydrate; Cellulase; Chitinases; GH; Glycoside hydrolase; Polysaccharide; Xylanase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Function, distribution, and annotation of characterized cellulases, xylanases, and chitinases from CAZy.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Feb;102(4):1629-1637. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-8778-y. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29359269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crystal Structure of Chitinase ChiW from Paenibacillus sp. str. FPU-7 Reveals a Novel Type of Bacterial Cell-Surface-Expressed Multi-Modular Enzyme Machinery.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 1;11(12):e0167310. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167310. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27907169 Free PMC article.
-
The GH10 and GH48 dual-functional catalytic domains from a multimodular glycoside hydrolase synergize in hydrolyzing both cellulose and xylan.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019 Dec 3;12:279. doi: 10.1186/s13068-019-1617-2. eCollection 2019. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019. PMID: 31827607 Free PMC article.
-
GeneHunt for rapid domain-specific annotation of glycoside hydrolases.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 12;9(1):10137. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46290-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31300677 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function analysis of Pseudomonas plant cell wall hydrolases.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1998;61:211-41. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60828-4. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9752722 Review.
Cited by
-
Carbohydrate Binding Modules: Diversity of Domain Architecture in Amylases and Cellulases From Filamentous Microorganisms.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Jul 31;8:871. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00871. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32850729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Bi-Modular GH19 Chitinase with Broad pH Stability from a Fibrolytic Intestinal Symbiont of Eisenia fetida, Cellulosimicrobium funkei HY-13.Biomolecules. 2021 Nov 21;11(11):1735. doi: 10.3390/biom11111735. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34827733 Free PMC article.
-
Function, distribution, and annotation of characterized cellulases, xylanases, and chitinases from CAZy.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Feb;102(4):1629-1637. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-8778-y. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29359269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycoside Hydrolases across Environmental Microbial Communities.PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 Dec 19;12(12):e1005300. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005300. eCollection 2016 Dec. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016. PMID: 27992426 Free PMC article.
-
Planctomycetes of the Genus Singulisphaera Possess Chitinolytic Capabilities.Microorganisms. 2024 Jun 22;12(7):1266. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12071266. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39065035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nielsen UN, Ayres E, Wall DH, Bardgett RD. Soil biodiversity and carbon cycling: a review and synthesis of studies examining diversity-function relationships. Eur J Soil Sci. 2011;62:105–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.2010.01314.x. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

