Effects of Ketamine-Propofol Mixture on Intraocular Pressure and Haemodynamics in Elderly Patients: A Randomised Double-Blind Trial
- PMID: 27366382
- PMCID: PMC4894100
- DOI: 10.5152/TJAR.2013.56
Effects of Ketamine-Propofol Mixture on Intraocular Pressure and Haemodynamics in Elderly Patients: A Randomised Double-Blind Trial
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to compare the effects of a ketamine-propofol mixture (ketofol) and propofol on intraocular pressure (IOP) and haemodynamics in elderly patients during anaesthetic management at each repeated measurement times.
Methods: Forty elderly ASA I and II patients were divided into two random groups and received either propofol (1.5 mg kg(-1); group P, n=20) or ketofol (1:1 single syringe mixture of 5 mg mL(-1) ketamine and 5 mg mL(-1) propofol; group KP, n=20). A proseal laryngeal mask airway (PLMA) was inserted 60 seconds after induction of anaesthesia. IOP, systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), and heart rate (HR) values were recorded at preinduction (t0), immediately following induction (t1), and at 1 (t2), 3 (t3), and 5 (t4) minutes after induction. Haemodynamic complications and the need for ephedrine were also recorded.
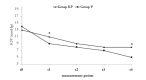
Results: Patient characteristics at the beginning of the procedure were similar between the groups. SBP and HR were significantly increased in group KP compared to group P at t1 and t4 (p=0.044). Induction of both anaesthetic agents significantly decreased the IOP values from the t0 (p=0.026). A significant decrease in IOP was found at t1 and t4 in group P compared to group KP (p=0.018). The total dose of ephedrine was statistically different in group P (p=0.034).
Conclusion: Ketofol can be an alternative agent to provide haemodynamic stability with a moderate decrease in IOP during anaesthesia induction in elderly patients.
Keywords: Intraocular pressure; elderly patient; hemodynamic; ketamine; propofol.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of effects of propofol and ketamine-propofol mixture (ketofol) on laryngeal mask airway insertion conditions and hemodynamics in elderly patients: a randomized, prospective, double-blind trial.J Anesth. 2013 Feb;27(1):12-7. doi: 10.1007/s00540-012-1484-5. Epub 2012 Sep 13. J Anesth. 2013. PMID: 22972566 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of Propofol and Ketamine-Propofol Mixture (Ketofol) on Laryngeal Tube-Suction II Conditions and Hemodynamics: A Randomized, Prospective, Double-Blind Trial.Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2013 Dec;75:39-43. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2013.06.003. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2013. PMID: 24465041 Free PMC article.
-
A clinical comparison of ketofol (ketamine and propofol admixture) versus propofol as an induction agent on quality of laryngeal mask airway insertion and hemodynamic stability in children.Anesth Essays Res. 2013 May-Aug;7(2):194-9. doi: 10.4103/0259-1162.118957. Anesth Essays Res. 2013. PMID: 25885832 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of intravenous induction with different doses of Esketamine combined with propofol and sufentanil on intraocular pressure among pediatric strabismus surgery: a randomized clinical trial.BMC Anesthesiol. 2023 Aug 15;23(1):275. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02238-2. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 37582704 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of ketofol versus propofol as an induction agent on ease of laryngeal mask airway insertion conditions and hemodynamic stability in pediatrics: an observational prospective cohort study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2019 Mar 20;19(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12871-019-0711-0. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019. PMID: 30894140 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effect of Ketamine/Propofol Admixture on Peri-Induction Hemodynamics: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Anesthesiol Res Pract. 2020 May 8;2020:9637412. doi: 10.1155/2020/9637412. eCollection 2020. Anesthesiol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 32454816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Dexmedetomidine Versus Ketamine-Propofol Combination for Sedation in Cataract Surgery.Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2015 Apr;43(2):84-90. doi: 10.5152/TJAR.2014.45220. Epub 2015 Feb 5. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2015. PMID: 27366473 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Assessment of Propofol and Ketamine on Hemodynamic Indices and Cerebral Oximetry of Pediatric Patients Undergoing Cardiac Catheterization.Anesth Pain Med. 2022 Dec 7;12(6):e128763. doi: 10.5812/aapm-128763. eCollection 2022 Dec. Anesth Pain Med. 2022. PMID: 36938113 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McGoldrick KE. The open globe: is an alternative to succinylcholine necessary? J Clin Anesth. 1993;5:1–4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0952-8180(93)90079-T. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sızmaz S, Çoban Karataş M, Altan Yaycioğlu R, Canan H, Cantürk S, Akova YA. Fakoemülsifikasyon sonrasında göz içi basınç değişimleri. Turkiye Klinikleri J Med Sci. 2012;32:1512–7. http://dx.doi.org/10.5336/medsci.2011-25614. - DOI
-
- Sator S, Wildling E, Schabernig C, Akramian J, Zulus E, Winkler M. Desflurane maintains intraocular pressure at an equivalent level to isoflurane and propofol during unstressed non -ophthalmic surgery. Br J Anaesth. 1998;80:243–4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bja/80.2.243. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Murphy DF. Anesthesia and intraocular pressure. Anesth Analg. 1985;64:520–30. http://dx.doi.org/10.1213/00000539-198505000-00013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sadove MS, Shulman M, Hatano S, Fevold N. Analgesic effects of ketamine administered in subdissociative doses. Anesth Analg. 1971;50:452–7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1213/00000539-197105000-00037. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources