Prevalence and severity of disordered mineral metabolism in patients with chronic kidney disease: A study from a tertiary care hospital in India
- PMID: 27366711
- PMCID: PMC4911834
- DOI: 10.4103/2230-8210.183457
Prevalence and severity of disordered mineral metabolism in patients with chronic kidney disease: A study from a tertiary care hospital in India
Abstract
Background: Disordered mineral metabolism is common complications of chronic kidney disease (CKD). However, there are limited data on the pattern of these disturbances in Indian CKD population.
Materials and methods: This was a prospective observational study of CKD-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD) over a period of 3 years. The biochemical markers of CKD-MBD, namely, calcium, phosphorus, alkaline phosphatase, intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH), and 25-hydoxyvitamin Vitamin D3 (25OHD), were measured in newly diagnosed CKD Stage 3-5 and prevalent CKD Stage 5D adult patients.
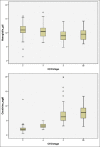
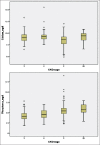
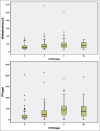
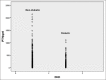
Results: A total of 462 patients of CKD Stage 3-5D were studied. The frequency of various biochemical abnormalities was hypocalcemia (23.8%), hypercalcemia (5.4%), hypophosphatemia (2.8%), hyperphosphatemia (55.4%), raised alkaline phosphatase (56.9%), secondary hyperparathyroidism (82.7%), and hypoparathyroidism (1.5%). 25OHD was done in 335 (72.5%) patients and 90.4% were found to have Vitamin D deficiency. About 70.6% of the patients had iPTH levels were above kidney disease outcomes quality initiative (KDOQI) target range. Nondiabetic CKD as compared to diabetic CKD had a higher alkaline phosphatase (P = 0.016), a higher iPTH (P = 0.001) a higher proportion of patients with iPTH above KDOQI target range (P = 0.09), and an elevated alkaline phosphatase (P = 0.004). The 25OHD levels were suggestive of severe Vitamin D deficiency in 33.7%, Vitamin D deficiency in 45.4%, and Vitamin D insufficiency in 11.3% patients. There was a significant positive correlation between iPTH with alkaline phosphatase (r = 0.572, P = 0.001), creatinine (r = 0.424, P = 0.001), and phosphorus (r = 0.241, P = 0.001) and a significant negative correlation with hemoglobin (r = -0.325, 0.001), age (r = -0.169, P = 0.002), and 25OHD (r = -0.126, P = 0.021). On multivariate logistic regression analysis, an elevated alkaline phosphatase was a significant predictor of hyperparathyroidism (odds ratio 9.7, 95% confidence interval 4.9-19.2, P = 0.001).
Conclusions: There was a high prevalence of CKD-MBD in Indian CKD patients. CKD-MBD is more common and more severe and has an early onset as compared to the western populations.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Vitamin D; chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder; hyperparathyroidism; hyperphosphatemia; hypocalcemia; mineral metabolism disorder.
Figures

References
-
- Coresh J, Astor BC, Greene T, Eknoyan G, Levey AS. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and decreased kidney function in the adult US population: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;41:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, Manzi J, Kusek JW, Eggers P, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA. 2007;298:2038–47. - PubMed
-
- Furuhashi T, Moroi M, Joki N, Hase H, Masai H, Kunimasa T, et al. The impact of chronic kidney disease as a predictor of major cardiac events in patients with no evidence of coronary artery disease. J Cardiol. 2010;55:328–36. - PubMed
-
- Keith DS, Nichols GA, Gullion CM, Brown JB, Smith DH. Longitudinal follow-up and outcomes among a population with chronic kidney disease in a large managed care organization. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164:659–63. - PubMed
-
- Moe S, Drüeke T, Cunningham J, Goodman W, Martin K, Olgaard K, et al. Definition, evaluation, and classification of renal osteodystrophy: A position statement from kidney disease: Improving global outcomes (KDIGO) Kidney Int. 2006;69:1945–53. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

