Abciximab as a bridging strategy to overcome morphine-prasugrel interaction in STEMI patients
- PMID: 27366874
- PMCID: PMC5061801
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.13053
Abciximab as a bridging strategy to overcome morphine-prasugrel interaction in STEMI patients
Abstract
Objective: The present study investigated whether the glycoprotein (GP)IIb/IIIa receptor blocker abciximab might be a successful bridging strategy to achieve adequate levels of platelet inhibition rapidly in cases where prasugrel is used in morphine-pretreated ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients.
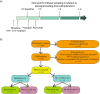
Methods: In a prospective observational cohort study, 32 patients presenting with STEMI were given prasugrel at a loading dose of 60 mg. Patients were stratified into four groups, according to morphine and/or abciximab use. Adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-induced platelet aggregation was measured at four time points: at baseline, and at 2 h, 1 day and 2 days after prasugrel loading.
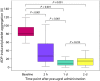
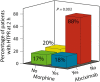
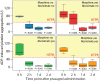
Results: Morphine use was associated with a three-fold higher level of ADP-induced platelet aggregation 2 h after prasugrel loading compared with no morphine/no abciximab (P = 0.019). However, when abciximab was infused in the catheterization laboratory, the effect of morphine on ADP-induced platelet aggregation disappeared (P = 0.884). This interaction was also seen in the presence of high on-treatment platelet reactivity (HTPR) at 2 h; while HTPR was seen in 88% of morphine users/no abciximab users, it was found in only 17-20% in the three other groups (P = 0.003). The effect of morphine disappeared by day 1 - 2.
Conclusion: The infusion of the GPIIb/IIIa receptor blocker abciximab allows immediate and efficient platelet inhibition in STEMI patients concomitantly receiving the oral ADP receptor blocker prasugrel and morphine.
Keywords: abciximab; morphine; platelet; prasugrel.
© 2016 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Platelet inhibition by abciximab bolus-only administration and oral ADP receptor antagonist loading in acute coronary syndrome patients: the blocking and bridging strategy.Thromb Res. 2013 Jul;132(1):e36-41. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2013.05.029. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Thromb Res. 2013. PMID: 23791395 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of prasugrel administration immediately after percutaneous coronary intervention in ST-elevation myocardial infarction.Thromb Haemost. 2017 Jan 5;117(1):99-104. doi: 10.1160/TH16-07-0569. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 27734075
-
Platelet aggregation inhibition with glycoprotein IIb--IIIa inhibitors.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2001 Apr;11(2):99-110. doi: 10.1023/a:1011216414539. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2001. PMID: 11406724 Review.
-
Prasugrel versus tirofiban bolus with or without short post-bolus infusion with or without concomitant prasugrel administration in patients with myocardial infarction undergoing coronary stenting: the FABOLUS PRO (Facilitation through Aggrastat By drOpping or shortening Infusion Line in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction compared to or on top of PRasugrel given at loading dOse) trial.JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2012 Mar;5(3):268-77. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2012.01.006. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2012. PMID: 22440491 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacodynamic and clinical trials of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors and potential relationship of results to dosing.Z Kardiol. 2003 Mar;92(3):213-8. doi: 10.1007/s00392-003-0895-6. Z Kardiol. 2003. PMID: 12658467 Review.
Cited by
-
Maintenance therapy with a P2Y12 receptor inhibitor after cangrelor in patients with acute coronary syndrome. The ELECTRA-SIRIO 2 investigators' viewpoint.Cardiol J. 2025;32(1):83-89. doi: 10.5603/cj.98323. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Cardiol J. 2025. PMID: 39776051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morphine in acute coronary syndrome: systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2019 Mar 15;9(3):e025232. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025232. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 30878985 Free PMC article.
-
Oral P2Y12 Inhibitors: Victims or Perpetrators? A Focused Review on Pharmacokinetic, Clinically Relevant Drug Interactions.Eur Cardiol. 2025 Jun 11;20:e17. doi: 10.15420/ecr.2025.12. eCollection 2025. Eur Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40556646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacodynamic Effects of a 6-Hour Regimen of Enoxaparin in Patients Undergoing Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PENNY PCI Study).Thromb Haemost. 2018 Jul;118(7):1250-1256. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1657768. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Thromb Haemost. 2018. PMID: 29874689 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of morphine use on oral P2Y12 platelet inhibitors in acute myocardial infarction: Meta-analysis.Indian Heart J. 2019 Mar-Apr;71(2):126-135. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2019.03.003. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Indian Heart J. 2019. PMID: 31280824 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siller‐Matula JM, Trenk D, Schror K, Gawaz M, Kristensen SD, Storey RF, et al. How to improve the concept of individualised antiplatelet therapy with P2Y12 receptor inhibitors – is an algorithm the answer? Thromb Haemost 2015; 113: 37–52. - PubMed
-
- Siller‐Matula JM, Trenk D, Krahenbuhl S, Michelson AD, Delle‐Karth G. Clinical implications of drug–drug interactions with P2Y12 receptor inhibitors. J Thromb Haemost 2014; 12: 2–13. - PubMed
-
- Hobl EL, Stimpfl T, Ebner J, Schoergenhofer C, Derhaschnig U, Sunder‐Plassmann R, et al. Morphine decreases clopidogrel concentrations and effects: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014; 63: 630–5. - PubMed
-
- Parodi G, Valenti R, Bellandi B, Migliorini A, Marcucci R, Comito V, et al. Comparison of prasugrel and ticagrelor loading doses in ST‐segment elevation myocardial infarction patients: RAPID (Rapid Activity of Platelet Inhibitor Drugs) primary PCI study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013; 61: 1601–6. - PubMed
-
- Parodi G, Bellandi B, Xanthopoulou I, Capranzano P, Capodanno D, Valenti R, et al. Morphine is associated with a delayed activity of oral antiplatelet agents in patients with ST‐elevation acute myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 2015; 8: e001593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

