Organoarsenical Biotransformations by Shewanella putrefaciens
- PMID: 27366920
- PMCID: PMC4984541
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.6b00235
Organoarsenical Biotransformations by Shewanella putrefaciens
Abstract
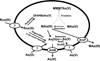
Microbes play a critical role in the global arsenic biogeocycle. Most studies have focused on redox cycling of inorganic arsenic in bacteria and archaea. The parallel cycles of organoarsenical biotransformations are less well characterized. Here we describe organoarsenical biotransformations in the environmental microbe Shewanella putrefaciens. Under aerobic growth conditions, S. putrefaciens reduced the herbicide MSMA (methylarsenate or MAs(V)) to methylarsenite (MAs(III)). Even though it does not contain an arsI gene, which encodes the ArsI C-As lyase, S. putrefaciens demethylated MAs(III) to As(III). It cleaved the C-As bond in aromatic arsenicals such as the trivalent forms of the antimicrobial agents roxarsone (Rox(III)), nitarsone (Nit(III)) and phenylarsenite (PhAs(III)), which have been used as growth promoters for poultry and swine. S. putrefaciens thiolated methylated arsenicals, converting MAs(V) into the more toxic metabolite monomethyl monothioarsenate (MMMTAs(V)), and transformed dimethylarsenate (DMAs(V)) into dimethylmonothioarsenate (DMMTAs(V)). It also reduced the nitro groups of Nit(V), forming p-aminophenyl arsenate (p-arsanilic acid or p-AsA(V)), and Rox(III), forming 3-amino-4-hydroxybenzylarsonate (3A4HBzAs(V)). Elucidation of organoarsenical biotransformations by S. putrefaciens provides a holistic appreciation of how these environmental pollutants are degraded.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of ArsEFG in Roxarsone and Nitarsone Detoxification and Resistance.Environ Sci Technol. 2019 Jun 4;53(11):6182-6191. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b01187. Epub 2019 May 14. Environ Sci Technol. 2019. PMID: 31059239
-
ArsH is an organoarsenical oxidase that confers resistance to trivalent forms of the herbicide monosodium methylarsenate and the poultry growth promoter roxarsone.Mol Microbiol. 2015 Jun;96(5):1042-52. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12988. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Mol Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25732202 Free PMC article.
-
Organoarsenical tolerance in Sphingobacterium wenxiniae, a bacterium isolated from activated sludge.Environ Microbiol. 2022 Feb;24(2):762-771. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.15599. Epub 2021 May 27. Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 33998126 Free PMC article.
-
The organoarsenical biocycle and the primordial antibiotic methylarsenite.Metallomics. 2016 Oct 1;8(10):1047-1055. doi: 10.1039/c6mt00168h. Metallomics. 2016. PMID: 27730229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New mechanisms of bacterial arsenic resistance.Biomed J. 2016 Feb;39(1):5-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2015.08.003. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Biomed J. 2016. PMID: 27105594 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Time Interval on Arsenic Toxicity to Paddy Field Cyanobacteria as Evident by Nitrogen Metabolism, Biochemical Constituent, and Exopolysaccharide Content.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021 May;199(5):2031-2046. doi: 10.1007/s12011-020-02289-3. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021. PMID: 32767030
-
Jacob-induced transcriptional inactivation of CREB promotes Aβ-induced synapse loss in Alzheimer's disease.EMBO J. 2023 Feb 15;42(4):e112453. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022112453. Epub 2023 Jan 3. EMBO J. 2023. PMID: 36594364 Free PMC article.
-
ArsV and ArsW provide synergistic resistance to the antibiotic methylarsenite.Environ Microbiol. 2021 Dec;23(12):7550-7562. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.15817. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34676971 Free PMC article.
-
Organoarsenicals inhibit bacterial peptidoglycan biosynthesis by targeting the essential enzyme MurA.Chemosphere. 2020 Sep;254:126911. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126911. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Chemosphere. 2020. PMID: 32957300 Free PMC article.
-
Glutathione Is Involved in the Reduction of Methylarsenate to Generate Antibiotic Methylarsenite in Enterobacter sp. Strain CZ-1.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Mar 22;88(6):e0246721. doi: 10.1128/aem.02467-21. Epub 2022 Jan 26. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35080903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li Y, Liu Z. Arsenic toxicity: toxicity, manifestation and geographical distribution. In: Chakrabarty N, editor. Arsenic Toxicity: Prevention and Treatment. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2016. pp. 45–78.
-
- Quinn JP, McMullan G. Carbon-arsenic bond cleavage by a newly isolated gram-negative bacterium, strain ASV2. Microbiology. 1995;141(Pt 3):721–725. - PubMed
-
- Naranmandura H, Rehman K, Le XC, Thomas DJ. Formation of methylated oxyarsenicals and thioarsenicals in wild-type and arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase knockout mice exposed to arsenate. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013;405(6):1885–1891. - PubMed
-
- Wang QQ, Thomas DJ, Naranmandura H. Importance of being thiomethylated: formation, fate, and effects of methylated thioarsenicals. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015;28(3):281–289. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

