Basal autophagy is pivotal for Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells' survival and growth revealing a new strategy for Hodgkin lymphoma treatment
- PMID: 27366944
- PMCID: PMC5216819
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.10300
Basal autophagy is pivotal for Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells' survival and growth revealing a new strategy for Hodgkin lymphoma treatment
Abstract
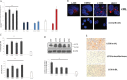
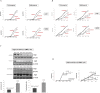
As current classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) treatment strategies have pronounced side-effects, specific inhibition of signaling pathways may offer novel strategies in cHL therapy. Basal autophagy, a regulated catabolic pathway to degrade cell's own components, is in cancer linked with both, tumor suppression or promotion. The finding that basal autophagy enhances tumor cell survival would thus lead to immediately testable strategies for novel therapies. Thus, we studied its contribution in cHL.We found constitutive activation of autophagy in cHL cell lines and primary tissue. The expression of key autophagy-relevant proteins (e.g. Beclin-1, ULK1) and LC3 processing was increased in cHL cells, even in lymphoma cases. Consistently, cHL cells exhibited elevated numbers of autophagic vacuoles and intact autophagic flux. Autophagy inhibition with chloroquine or inactivation of ATG5 induced apoptosis and reduced proliferation of cHL cells. Chloroquine-mediated inhibition of basal autophagy significantly impaired HL growth in-vivo in NOD SCID γc-/- (NSG) mice. We found that basal autophagy plays a pivotal role in sustaining mitochondrial function.We conclude that cHL cells require basal autophagy for growth, survival and sustained metabolism making them sensitive to autophagy inhibition. This suggests basal autophagy as useful target for new strategies in cHL treatment.
Keywords: B-cell lymphoma; Hodgkin lymphoma; autophagy; lymphoma pathogenesis; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Hellman S. Brief Consideration of Thomas Hodgkin and His Times. In: Hoppe RT, Mauch PT, Armitage JO, Diehl V, Weiss LM, editors. Hodgkin Lymphoma. 2. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007.
-
- Küppers R. The biology of Hodgkin's lymphoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:15–27. - PubMed
-
- Greaves W, Xiao L, Sanchez-Espiridion B, Kunkalla K, Dave KS, Liang CS, Singh RR, Younes A, Medeiros LJ, Vega F. Detection of ABCC1 expression in classical Hodgkin lymphoma is associated with increased risk of treatment failure using standard chemotherapy protocols. Hematol Oncol. 2012;5:47. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lowry L, Hoskin P, Linch D. Developments in the management of Hodgkin's lymphoma. Lancet. 2010;375:786–788. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

