Induction of Excess Centrosomes in Neural Progenitor Cells during the Development of Radiation-Induced Microcephaly
- PMID: 27367050
- PMCID: PMC4930206
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158236
Induction of Excess Centrosomes in Neural Progenitor Cells during the Development of Radiation-Induced Microcephaly
Abstract
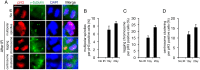
The embryonic brain is one of the tissues most vulnerable to ionizing radiation. In this study, we showed that ionizing radiation induces apoptosis in the neural progenitors of the mouse cerebral cortex, and that the surviving progenitor cells subsequently develop a considerable amount of supernumerary centrosomes. When mouse embryos at Day 13.5 were exposed to γ-rays, brains sizes were reduced markedly in a dose-dependent manner, and these size reductions persisted until birth. Immunostaining with caspase-3 antibodies showed that apoptosis occurred in 35% and 40% of neural progenitor cells at 4 h after exposure to 1 and 2 Gy, respectively, and this was accompanied by a disruption of the apical layer in which mitotic spindles were positioned in unirradiated mice. At 24 h after 1 Gy irradiation, the apoptotic cells were completely eliminated and proliferation was restored to a level similar to that of unirradiated cells, but numerous spindles were localized outside the apical layer. Similarly, abnormal cytokinesis, which included multipolar division and centrosome clustering, was observed in 19% and 24% of the surviving neural progenitor cells at 48 h after irradiation with 1 and 2 Gy, respectively. Because these cytokinesis aberrations derived from excess centrosomes result in growth delay and mitotic catastrophe-mediated cell elimination, our findings suggest that, in addition to apoptosis at an early stage of radiation exposure, radiation-induced centrosome overduplication could contribute to the depletion of neural progenitors and thereby lead to microcephaly.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
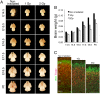
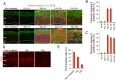
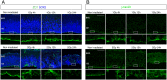
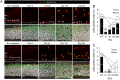
Similar articles
-
A possible role for centrosome overduplication in radiation-induced cell death.Oncogene. 2000 Nov 2;19(46):5281-90. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203902. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11077445
-
High LET radiation amplifies centrosome overduplication through a pathway of γ-tubulin monoubiquitination.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013 Jun 1;86(2):358-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.01.010. Epub 2013 Feb 20. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013. PMID: 23433796
-
Involvement of centrosome amplification in radiation-induced mitotic catastrophe.Cell Cycle. 2007 Feb 1;6(3):364-70. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.3.3834. Epub 2007 Feb 11. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17297293
-
Emerging connection between centrosome and DNA repair machinery.J Radiat Res. 2009 Jul;50(4):295-301. doi: 10.1269/jrr.09039. Epub 2009 Jun 20. J Radiat Res. 2009. PMID: 19542690 Review.
-
A centrosomal view of CNS growth.Development. 2018 Nov 6;145(21):dev170613. doi: 10.1242/dev.170613. Development. 2018. PMID: 30401784 Review.
Cited by
-
Counter-Balance Between Gli3 and miR-7 Is Required for Proper Morphogenesis and Size Control of the Mouse Brain.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Aug 17;12:259. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00259. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30210296 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage and repair: underlying mechanisms leading to microcephaly.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Oct 10;11:1268565. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1268565. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37881689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Puma, noxa, p53, and p63 differentially mediate stress pathway induced apoptosis.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jun 30;12(7):659. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03902-6. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34193827 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming and differentiation-dependent transcriptional alteration of DNA damage response and apoptosis genes in human induced pluripotent stem cells.J Radiat Res. 2019 Nov 22;60(6):719-728. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrz057. J Radiat Res. 2019. PMID: 31665364 Free PMC article.
-
Microcephaly.Children (Basel). 2017 Jun 9;4(6):47. doi: 10.3390/children4060047. Children (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28598357 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nowak E, Etienne O, Millet P, Lages CS, Mathieu C, Mouthon MA, et al. Radiation-induced H2AX phosphorylation and neural precursor apoptosis in the developing brain of mice. Radiat Res. 2006; 165(2):155–64. Epub 2006/01/27. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

