Prognostic significance of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 and 5b expression in Epstein-Barr virus-positive patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 27367207
- PMCID: PMC5055175
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.804
Prognostic significance of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 and 5b expression in Epstein-Barr virus-positive patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
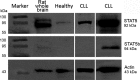
Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) proteins have been intensively studied in hematologic malignancies, and the efficacy of agents against STATs in lymphomas is already under research. We investigated the expression of total STAT5 and STAT5b in peripheral blood samples of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in correlation with the presence of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) and its major oncoprotein (latent membrane protein 1, LMP1). The EBV load was measured in the peripheral blood by real-time PCR for the BXLF1 gene and the levels of LMP1 by PCR and ELISA. Western blotting was performed for total STAT5 and STAT5b in protein extracts. STAT5b was only expressed in patients (not in healthy subjects) and STAT5 but particularly STAT5b expression was correlated with the presence of the virus (77.3% vs. 51.2%, P = 0.006 for STAT5b) and to the expression of LMP1 (58.3% vs. 21.6%, P = 0.011 for STAT5b). Moreover, the expression of STAT5b and the presence of EBV and LMP1 were strongly negatively correlated with the overall survival of the patients (log-rank test P = 0.011, 0.015, 0.006, respectively). Double positive (for EBV and STAT5b) patients had the lowest overall survival (log-rank test P = 0.013). This is the first report of a survival disadvantage of EBV+ patients with CLL, and the first time that STAT5b expression is correlated with survival. The correlation of STAT5 expression with the presence of the virus, along with our survival correlations defines a subgroup of patients with CLL that may benefit from anti-STAT agents.
Keywords: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia; Epstein-Barr virus; latent membrane protein 1; signal transducer and activator of transcription 5.
© 2016 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Grimley, P. M. , Dong F., and Rui H.. 1999. Stat5a and Stat5b: Fraternal twins of signal transduction and transcriptional activation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 10: 131–157. - PubMed
-
- Ferbeyre, G. , and Moriggl R.. 2011. The role of Stat5 transcription factors as tumor suppressors or oncogenes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1815:104–114. - PubMed
-
- Yu, H. , and Jove R.. 2004. The STATs of cancer–new molecular targets come of age. Nat. Rev. Cancer 4:97–105. - PubMed
-
- Hong, D. S. , Younes A., Fayad L., Fowler N. H., Hagemeister F. B., Mistry R., et al. 2013. A phase I study of ISIS 481464 (AZD9150), a first‐in‐human, first‐in‐class, antisense oligonucleotide inhibitor of STAT3, in patients with advanced cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 31(suppl):8523.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

