Binge-Eating Disorder in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 27367316
- PMCID: PMC5637727
- DOI: 10.7326/M15-2455
Binge-Eating Disorder in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The best treatment options for binge-eating disorder are unclear.
Purpose: To summarize evidence about the benefits and harms of psychological and pharmacologic therapies for adults with binge-eating disorder.
Data sources: English-language publications in EMBASE, the Cochrane Library, Academic OneFile, CINAHL, and ClinicalTrials.gov through 18 November 2015, and in MEDLINE through 12 May 2016.
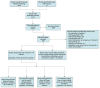
Study selection: 9 waitlist-controlled psychological trials and 25 placebo-controlled trials that evaluated pharmacologic (n = 19) or combination (n = 6) treatment. All were randomized trials with low or medium risk of bias.
Data extraction: 2 reviewers independently extracted trial data, assessed risk of bias, and graded strength of evidence.
Data synthesis: Therapist-led cognitive behavioral therapy, lisdexamfetamine, and second-generation antidepressants (SGAs) decreased binge-eating frequency and increased binge-eating abstinence (relative risk, 4.95 [95% CI, 3.06 to 8.00], 2.61 [CI, 2.04 to 3.33], and 1.67 [CI, 1.24 to 2.26], respectively). Lisdexamfetamine (mean difference [MD], -6.50 [CI, -8.82 to -4.18]) and SGAs (MD, -3.84 [CI, -6.55 to -1.13]) reduced binge-eating-related obsessions and compulsions, and SGAs reduced symptoms of depression (MD, -1.97 [CI, -3.67 to -0.28]). Headache, gastrointestinal upset, sleep disturbance, and sympathetic nervous system arousal occurred more frequently with lisdexamfetamine than placebo (relative risk range, 1.63 to 4.28). Other forms of cognitive behavioral therapy and topiramate also increased abstinence and reduced binge-eating frequency and related psychopathology. Topiramate reduced weight and increased sympathetic nervous system arousal, and lisdexamfetamine reduced weight and appetite.
Limitations: Most study participants were overweight or obese white women aged 20 to 40 years. Many treatments were examined only in single studies. Outcomes were measured inconsistently across trials and rarely assessed beyond end of treatment.
Conclusion: Cognitive behavioral therapy, lisdexamfetamine, SGAs, and topiramate reduced binge eating and related psychopathology, and lisdexamfetamine and topiramate reduced weight in adults with binge-eating disorder.
Primary funding source: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
Figures


Comment in
-
Binge-Eating Disorder Comes of Age.Ann Intern Med. 2016 Sep 20;165(6):445-6. doi: 10.7326/M16-1398. Epub 2016 Jun 28. Ann Intern Med. 2016. PMID: 27366876 No abstract available.
-
Binge-Eating Disorder in Adults.Ann Intern Med. 2017 Feb 7;166(3):231-232. doi: 10.7326/L16-0621. Ann Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28166552 No abstract available.
-
Binge-Eating Disorder in Adults.Ann Intern Med. 2017 Feb 7;166(3):230-231. doi: 10.7326/L16-0622. Ann Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28166553 No abstract available.
References
-
- Nicdao EG, Hong S, Takeuchi DT. Prevalence and correlates of eating disorders among Asian Americans: results from the National Latino and Asian American Study. Int J Eat Disord. 2007;40(Suppl):S22–6. - PubMed
-
- Bruce B, Wilfley D. Binge eating among the overweight population: a serious and prevalent problem. J Am Diet Assoc. 1996;96:58–61. - PubMed
-
- Spitzer RL, Yanovski S, Wadden T, Wing R, Marcus MD, Stunkard A, et al. Binge eating disorder: its further validation in a multisite study. Int J Eat Disord. 1993;13:137–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
