RINT1 functions as a multitasking protein at the crossroads between genomic stability, ER homeostasis, and autophagy
- PMID: 27367497
- PMCID: PMC4968223
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1191730
RINT1 functions as a multitasking protein at the crossroads between genomic stability, ER homeostasis, and autophagy
Abstract
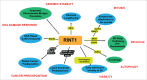
RINT1 was first identified as an RAD50-interacting protein and its function was therefore linked to the maintenance of genomic stability. It was also shown that RINT1 was a key player in ER-Golgi trafficking as a member of an ER tethering complex interacting with STX18. However, due to early embryonic lethality of rint1-null mice, the in vivo functions of RINT1 remained for the most part elusive. We recently described the consequences of Rint1 inactivation in various neuronal cells of the central nervous system. We observed that lack of RINT1 in vivo triggers genomic instability and ER stress leading to depletion of the neural progenitor pool and neurodegeneration. Surprisingly, we also observed inhibition of autophagy in RINT1-deficient neurons, indicating an involvement of RINT1 in the regulation of neuronal autophagy. Here, we summarize our main RINT1 findings and discuss its putative roles in autophagy.
Keywords: ER stress; ER-Golgi homeostasis; RINT1; autophagy inhibition; genomic stability; neurodegeneration.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rint1 inactivation triggers genomic instability, ER stress and autophagy inhibition in the brain.Cell Death Differ. 2016 Mar;23(3):454-68. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.113. Epub 2015 Sep 18. Cell Death Differ. 2016. PMID: 26383973 Free PMC article.
-
The intersection of Golgi-ER retrograde and autophagic trafficking.Autophagy. 2014 Jan;10(1):180-1. doi: 10.4161/auto.26917. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Autophagy. 2014. PMID: 24246972 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Rint1 as a modifier of intestinal tumorigenesis and cancer risk.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 6;12(3):e0172247. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172247. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28264000 Free PMC article.
-
The soluble reticulophagy receptor CALCOCO1 is also a Golgiphagy receptor.Autophagy. 2021 Aug;17(8):2051-2052. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1940610. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Autophagy. 2021. PMID: 34162311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p97/p47-Mediated biogenesis of Golgi and ER.J Biochem. 2005 Feb;137(2):115-9. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvi028. J Biochem. 2005. PMID: 15749824 Review.
Cited by
-
Syntaxin 18 regulates the DNA damage response and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition to promote radiation resistance of lung cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Jun 6;13(6):529. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04978-4. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35668077 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Neurotoxin MPTP and Neuroprotector Isatin on the Profile of Ubiquitinated Brain Mitochondrial Proteins.Cells. 2018 Jul 31;7(8):91. doi: 10.3390/cells7080091. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30065189 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Golgi complex proteins in cell division and consequences of their dysregulation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jan 7;12:1513472. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1513472. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 39839669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FUT8-mediated aberrant N-glycosylation of SEMA7A promotes head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression.Int J Oral Sci. 2024 Mar 28;16(1):26. doi: 10.1038/s41368-024-00289-w. Int J Oral Sci. 2024. PMID: 38548747 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine-Induced Cytotoxicity and Extracellular Matrix Abnormalities in Hepatocytes Derived From RAD50-Interacting Protein 1-Deficient Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.FASEB J. 2025 Aug 15;39(15):e70909. doi: 10.1096/fj.202500742R. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 40762441 Free PMC article.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
