Quality Evaluation of Scrophulariae Radix Processed by Different 'Sweating' Methods Based on Simultaneous Determination of Multiple Bioactive Constituents Combined with Grey Relational Analysis
- PMID: 27367656
- PMCID: PMC6273517
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21070850
Quality Evaluation of Scrophulariae Radix Processed by Different 'Sweating' Methods Based on Simultaneous Determination of Multiple Bioactive Constituents Combined with Grey Relational Analysis
Abstract
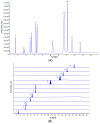
Scrophulariae Radix is one of the most popular traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs), which needs to be processed by 'sweating' methods. Primary processing of Scrophulariae Radix is an important link which closely relates to the quality of products in this TCM. To facilitate selection of the suitable 'sweating' processing method for Scrophulariae Radix, in this study the quality of Scrophulariae Radix processed by different 'sweating' methods was evaluated based on simultaneous determination of multiple bioactive constituents combined with grey relational analysis. The contents of iridoid glycosides, phenylpropanoid glycosides, and organic acids in Scrophulariae Radix processed by different 'sweating' methods were simultaneously determined using ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole-linear ion trap mass spectrometry (UPLC-QTRAP-MS/MS). Furthermore, grey relational analysis (GRA) was performed to evaluate the 'sweating' processed samples according to the contents of twelve constituents. All of the results demonstrated that the quality of Scrophulariae Radix processed by oven drying at 35 °C and 'sweating' for three days was better. The developed method was useful for the overall assessment on quality of Scrophulariae Radix, and this study may provide the foundation and support for 'sweating' processing of Scrophulariae Radix in normalization and standardization.
Keywords: Scrophulariae Radix; UPLC-QTRAP-MS/MS; grey relational analysis; simultaneous determination; ‘sweating’.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of Chemical Constituents in Scrophulariae Radix Processed by Different Methods based on UFLC-MS Combined with Multivariate Statistical Analysis.J Chromatogr Sci. 2018 Feb 1;56(2):122-130. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/bmx090. J Chromatogr Sci. 2018. PMID: 29140413
-
Simultaneous Determination of Iridoid Glycosides, Phenylpropanoid Glycosides, Organic Acids, Nucleosides and Amino Acids in Scrophulariae Radix Processed by Different Processing Methods by HPLC-QTRAP-MS/MS.J Chromatogr Sci. 2022 Mar 23;60(3):232-242. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/bmab056. J Chromatogr Sci. 2022. PMID: 34100538
-
Dynamic changes of metabolite accumulation in Scrophulariae Radix based on liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry combined with multivariate statistical analysis.J Sep Sci. 2017 Jul;40(14):2883-2894. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201700129. Epub 2017 Jun 1. J Sep Sci. 2017. PMID: 28493542
-
[Chemical constituents, pharmacological activities, processing and clinical application of traditional Chinese medicine Scrophulariae Radix: a review].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Aug;48(16):4302-4319. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230123.201. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37802857 Review. Chinese.
-
Scrophulariae Radix: An Overview of Its Biological Activities and Nutraceutical and Pharmaceutical Applications.Molecules. 2021 Aug 30;26(17):5250. doi: 10.3390/molecules26175250. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34500684 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative efficacy of sweated and non-sweated Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge. extracts on acute myocardial ischemia via regulating the PPARα/RXRα/NF-κB signaling pathway.Heliyon. 2024 May 27;10(11):e31923. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31923. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38845919 Free PMC article.
-
The sweating process promotes toxigenic fungi expansion and increases the risk of combined contamination of mycotoxins in Radix Dipsaci.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jun 6;15:1394774. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1394774. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38903800 Free PMC article.
-
Quality Evaluation of Ophiopogonis Radix from Two Different Producing Areas.Molecules. 2019 Sep 4;24(18):3220. doi: 10.3390/molecules24183220. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31487946 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Different Processing Methods on the Chemical Constituents of Scrophulariae Radix as Revealed by 2D NMR-Based Metabolomics.Molecules. 2022 Jul 22;27(15):4687. doi: 10.3390/molecules27154687. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35897871 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of Key Components for Melanogenesis Inhibition of Polygonum cuspidatum Extract Based on the Spectrum-Effect Relationship and Molecular Docking.Molecules. 2024 Feb 15;29(4):857. doi: 10.3390/molecules29040857. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38398609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xie X.Y., Xia C.S. Advances in studies on chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Scrophularia ningpoensis Hemsl. Asia Pac. Tradit. Med. 2010;6:121–125.
-
- Gu W.L., Chen C.X., Wu Q., Lu J., Liu Y., Zhang S.J. Effects of Chinese herb medicine Radix Scrophulariae on ventricular remodeling. Die Pharm. 2010;65:770–775. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

