In Silico Mining for Antimalarial Structure-Activity Knowledge and Discovery of Novel Antimalarial Curcuminoids
- PMID: 27367660
- PMCID: PMC6273176
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21070853
In Silico Mining for Antimalarial Structure-Activity Knowledge and Discovery of Novel Antimalarial Curcuminoids
Abstract
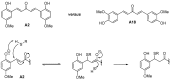
Malaria is a parasitic tropical disease that kills around 600,000 patients every year. The emergence of resistant Plasmodium falciparum parasites to artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) represents a significant public health threat, indicating the urgent need for new effective compounds to reverse ACT resistance and cure the disease. For this, extensive curation and homogenization of experimental anti-Plasmodium screening data from both in-house and ChEMBL sources were conducted. As a result, a coherent strategy was established that allowed compiling coherent training sets that associate compound structures to the respective antimalarial activity measurements. Seventeen of these training sets led to the successful generation of classification models discriminating whether a compound has a significant probability to be active under the specific conditions of the antimalarial test associated with each set. These models were used in consensus prediction of the most likely active from a series of curcuminoids available in-house. Positive predictions together with a few predicted as inactive were then submitted to experimental in vitro antimalarial testing. A large majority from predicted compounds showed antimalarial activity, but not those predicted as inactive, thus experimentally validating the in silico screening approach. The herein proposed consensus machine learning approach showed its potential to reduce the cost and duration of antimalarial drug discovery.
Keywords: Michael addition; Plasmodium falciparum; antimalarial; curcuminoid; in silico; quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSAR); thioredoxin reductase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
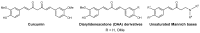
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

