Computational Identification of the Paralogs and Orthologs of Human Cytochrome P450 Superfamily and the Implication in Drug Discovery
- PMID: 27367670
- PMCID: PMC4964396
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17071020
Computational Identification of the Paralogs and Orthologs of Human Cytochrome P450 Superfamily and the Implication in Drug Discovery
Abstract
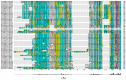
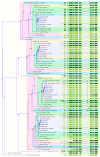
The human cytochrome P450 (CYP) superfamily consisting of 57 functional genes is the most important group of Phase I drug metabolizing enzymes that oxidize a large number of xenobiotics and endogenous compounds, including therapeutic drugs and environmental toxicants. The CYP superfamily has been shown to expand itself through gene duplication, and some of them become pseudogenes due to gene mutations. Orthologs and paralogs are homologous genes resulting from speciation or duplication, respectively. To explore the evolutionary and functional relationships of human CYPs, we conducted this bioinformatic study to identify their corresponding paralogs, homologs, and orthologs. The functional implications and implications in drug discovery and evolutionary biology were then discussed. GeneCards and Ensembl were used to identify the paralogs of human CYPs. We have used a panel of online databases to identify the orthologs of human CYP genes: NCBI, Ensembl Compara, GeneCards, OMA ("Orthologous MAtrix") Browser, PATHER, TreeFam, EggNOG, and Roundup. The results show that each human CYP has various numbers of paralogs and orthologs using GeneCards and Ensembl. For example, the paralogs of CYP2A6 include CYP2A7, 2A13, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C18, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, 2F1, 2J2, 2R1, 2S1, 2U1, and 2W1; CYP11A1 has 6 paralogs including CYP11B1, 11B2, 24A1, 27A1, 27B1, and 27C1; CYP51A1 has only three paralogs: CYP26A1, 26B1, and 26C1; while CYP20A1 has no paralog. The majority of human CYPs are well conserved from plants, amphibians, fishes, or mammals to humans due to their important functions in physiology and xenobiotic disposition. The data from different approaches are also cross-validated and validated when experimental data are available. These findings facilitate our understanding of the evolutionary relationships and functional implications of the human CYP superfamily in drug discovery.
Keywords: bioinformatics; comparative genomics; drug metabolism; homolog; human CYP; ortholog; paralog.
Figures












References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

