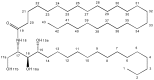
Fourier Transform Mass Spectrometry and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Analysis for the Rapid and Accurate Characterization of Hexacosanoylceramide
- PMID: 27367671
- PMCID: PMC4964400
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17071024
Fourier Transform Mass Spectrometry and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Analysis for the Rapid and Accurate Characterization of Hexacosanoylceramide
Abstract
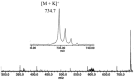
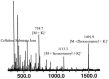
Ceramides are a central unit of all sphingolipids which have been identified as sites of biological recognition on cellular membranes mediating cell growth and differentiation. Several glycosphingolipids have been isolated, displaying immunomodulatory and anti-tumor activities. These molecules have generated considerable interest as potential vaccine adjuvants in humans. Accurate analyses of these and related sphingosine analogues are important for the characterization of structure, biological function, and metabolism. We report the complementary use of direct laser desorption ionization (DLDI), sheath flow electrospray ionization (ESI) Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (FTICR MS) and high-field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analysis for the rapid, accurate identification of hexacosanoylceramide and starting materials. DLDI does not require stringent sample preparation and yields representative ions. Sheath-flow ESI yields ions of the product and byproducts and was significantly better than monospray ESI due to improved compound solubility. Negative ion sheath flow ESI provided data of starting materials and products all in one acquisition as hexacosanoic acid does not ionize efficiently when ceramides are present. NMR provided characterization of these lipid molecules complementing the results obtained from MS analyses. NMR data was able to differentiate straight chain versus branched chain alkyl groups not easily obtained from mass spectrometry.
Keywords: Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (FTICR MS); adjuvants; ceramides; direct laser desorption ionization; electrospray ionization; nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR); sphingolipids.
Figures






References
-
- Miller H.C., Esselman W.S. Modulation of the immune response by antigen-reactive lymphocytes after cultivation with gangliosides. J. Immunol. 1975;115:839–843. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

