Amperometric Non-Enzymatic Hydrogen Peroxide Sensor Based on Aligned Zinc Oxide Nanorods
- PMID: 27367693
- PMCID: PMC4970054
- DOI: 10.3390/s16071004
Amperometric Non-Enzymatic Hydrogen Peroxide Sensor Based on Aligned Zinc Oxide Nanorods
Abstract
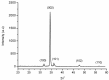
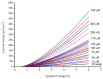
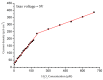
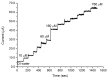
Zinc oxide (ZnO) nanorods (NRs) have been synthesized via the hydrothermal process. The NRs were grown over a conductive glass substrate. A non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor for hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂), based on the prepared ZnO NRs, was examined through the use of current-voltage measurements. The measured currents, as a function of H₂O₂ concentrations ranging from 10 μM to 700 μM, revealed two distinct behaviours and good performance, with a lower detection limit (LOD) of 42 μM for the low range of H₂O₂ concentrations (first region), and a LOD of 143.5 μM for the higher range of H₂O₂ concentrations (second region). The prepared ZnO NRs show excellent electrocatalytic activity. This enables a measurable and stable output current. The results were correlated with the oxidation process of the H₂O₂ and revealed a good performance for the ZnO NR non-enzymatic H₂O₂ sensor.
Keywords: hydrogen peroxide; nanorods; non-enzymatic biosensor; zinc oxide.
Figures
References
-
- Deng Y., Zuo Y. Factors affecting the levels of hydrogen peroxide in rainwater. Atmos. Environ. 1999;33:1469–1478. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(98)00239-8. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

