Leucine-Enriched Essential Amino Acids Augment Mixed Protein Synthesis, But Not Collagen Protein Synthesis, in Rat Skeletal Muscle after Downhill Running
- PMID: 27367725
- PMCID: PMC4963875
- DOI: 10.3390/nu8070399
Leucine-Enriched Essential Amino Acids Augment Mixed Protein Synthesis, But Not Collagen Protein Synthesis, in Rat Skeletal Muscle after Downhill Running
Abstract
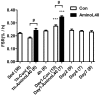
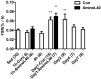
Mixed and collagen protein synthesis is elevated for as many as 3 days following exercise. Immediately after exercise, enhanced amino acid availability increases synthesis of mixed muscle protein, but not muscle collagen protein. However, the potential for synergic effects of amino acid ingestion with exercise on both mixed and collagen protein synthesis remains unclear. We investigated muscle collagen protein synthesis in rats following post-exercise ingestion of leucine-enriched essential amino acids. We determined fractional protein synthesis rates (FSR) at different time points following exercise. Mixed protein and collagen protein FSRs in skeletal muscle were determined by measuring protein-bound enrichments of hydroxyproline and proline, and by measuring the intracellular enrichment of proline, using injections of flooding d₃-proline doses. A leucine-enriched mixture of essential amino acids (or distilled water as a control) was administrated 30 min or 1 day post-exercise. The collagen protein synthesis in the vastus lateralis was elevated for 2 days after exercise. Although amino acid administration did not increase muscle collagen protein synthesis, it did lead to augmented mixed muscle protein synthesis 1 day following exercise. Thus, contrary to the regulation of mixed muscle protein synthesis, muscle collagen protein synthesis is not affected by amino acid availability after damage-inducing exercise.
Keywords: Leucine-enriched essential amino acids; downhill running; mammalian target of rapamycin; mixed muscle protein synthesis; muscle collagen protein synthesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Leucine-enriched essential amino acids attenuate muscle soreness and improve muscle protein synthesis after eccentric contractions in rats.Amino Acids. 2015 Jun;47(6):1193-201. doi: 10.1007/s00726-015-1946-9. Epub 2015 Mar 14. Amino Acids. 2015. PMID: 25772815 Free PMC article.
-
Leucine-enriched essential amino acid and carbohydrate ingestion following resistance exercise enhances mTOR signaling and protein synthesis in human muscle.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Feb;294(2):E392-400. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00582.2007. Epub 2007 Dec 4. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008. PMID: 18056791 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A high proportion of leucine is required for optimal stimulation of the rate of muscle protein synthesis by essential amino acids in the elderly.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Aug;291(2):E381-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00488.2005. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006. PMID: 16507602 Clinical Trial.
-
Leucine-enriched nutrients and the regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin signalling and human skeletal muscle protein synthesis.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2008 May;11(3):222-6. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e3282fa17fb. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2008. PMID: 18403916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Amino Acid Nutrition in the Prevention and Treatment of Sarcopenia].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018;138(10):1277-1283. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00091-4. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018. PMID: 30270272 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Leucine-enriched amino acids maintain peripheral mTOR-Rheb localization independent of myofibrillar protein synthesis and mTORC1 signaling postexercise.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2020 Jul 1;129(1):133-143. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00241.2020. Epub 2020 Jun 11. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2020. PMID: 32525432 Free PMC article.
-
Within-Day Amino Acid Intakes and Nitrogen Balance in Male Collegiate Swimmers during the General Preparation Phase.Nutrients. 2018 Nov 20;10(11):1809. doi: 10.3390/nu10111809. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30463354 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between Collagen and Lidocaine Intramuscular Injections in Terms of Their Efficiency in Decreasing Myofascial Pain within Masseter Muscles: A Randomized, Single-Blind Controlled Trial.Pain Res Manag. 2018 Jun 3;2018:8261090. doi: 10.1155/2018/8261090. eCollection 2018. Pain Res Manag. 2018. PMID: 29973970 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Leucine-Enriched Essential Amino Acids Improve Recovery from Post-Exercise Muscle Damage Independent of Increases in Integrated Myofibrillar Protein Synthesis in Young Men.Nutrients. 2020 Apr 11;12(4):1061. doi: 10.3390/nu12041061. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32290521 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

