CLIF-SOFA score and SIRS are independent prognostic factors in patients with hepatic encephalopathy due to alcoholic liver cirrhosis
- PMID: 27367990
- PMCID: PMC4937904
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003935
CLIF-SOFA score and SIRS are independent prognostic factors in patients with hepatic encephalopathy due to alcoholic liver cirrhosis
Abstract
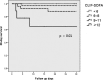
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a complication associated with worst prognosis in decompensated liver cirrhosis (LC) patients. Previous studies have identified prognostic factors for HE, and recent studies reported an association between systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and liver disease. This study aimed to identify prognostic factors for 30-day mortality in alcoholic LC patients with HE who visited the emergency department (ED).This was a retrospective study of alcoholic LC patients with HE from January 1, 2010, to April 30, 2015. The baseline characteristics, complications of portal hypertension, laboratory values, Child-Pugh class, Model for End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) score, chronic liver failure-sequential organ failure assessment (CLIF-SOFA) score, and SIRS criteria were assessed. The presence of 2 or more SIRS criteria was considered SIRS. The primary outcomes were 30-day mortality and prognostic factors for patients with HE visiting the ED.In total, 105 patients who met the inclusion criteria were analyzed. Overall, the 30-day mortality rate was 6.7% (7 patients).Significant variables were hepatorenal syndrome, international normalized ratio, white blood cell count, total bilirubin level, MELD score CLIF-SOFA score, and SIRS in univariate analysis. CLIF-SOFA score and SIRS were the significant factors in the multivariate analysis (hazard ratio 5.56, 15.98; 95% confidence interval 1.18-26.18, 1.58-161.37; P = 0.03, P = 0.02). The mortality rates differed according to the CLIF-SOFA score (P < 0.01).The CLIF-SOFA score and SIRS in alcoholic LC patients with HE visiting the ED are independent predictors of 30-day mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CLIF-SOFA scoring system accurately predicts short-term mortality in acutely decompensated patients with alcoholic cirrhosis: a retrospective analysis.Liver Int. 2015 Jan;35(1):46-57. doi: 10.1111/liv.12683. Epub 2014 Oct 1. Liver Int. 2015. PMID: 25203221 Clinical Trial.
-
Characteristics, risk factors, and mortality of cirrhotic patients hospitalized for hepatic encephalopathy with and without acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF).J Hepatol. 2014 Feb;60(2):275-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.10.004. Epub 2013 Oct 12. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24128414
-
Prognostication of critically ill patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure using the Chronic Liver Failure-Sequential Organ Failure Assessment: A Canadian retrospective study.J Crit Care. 2016 Dec;36:234-239. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2016.08.003. Epub 2016 Aug 10. J Crit Care. 2016. PMID: 27569253
-
Advances in management and prognostication in critically ill cirrhotic patients.Curr Opin Crit Care. 2014 Apr;20(2):210-7. doi: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000067. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2014. PMID: 24514101 Review.
-
Head-to-head comparison of qSOFA and SIRS criteria in predicting the mortality of infected patients in the emergency department: a meta-analysis.Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2018 Jul 11;26(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13049-018-0527-9. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2018. PMID: 29996880 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Outcomes of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Mechanically Ventilated Patients With Cirrhosis.Crit Care Explor. 2019 Sep 17;1(9):e0040. doi: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000000040. eCollection 2019 Sep. Crit Care Explor. 2019. PMID: 32166282 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome and model for end-stage liver disease score accurately predict the in-hospital mortality of black African patients with decompensated cirrhosis at initial hospitalization: a retrospective cohort study.Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2018 Apr 9;11:143-152. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S140655. eCollection 2018. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29670387 Free PMC article.
-
The Significant Morbidity and Mortality Indicators in Patients of Cirrhosis.Cureus. 2022 Jan 14;14(1):e21226. doi: 10.7759/cureus.21226. eCollection 2022 Jan. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35174029 Free PMC article.
-
KASL clinical practice guidelines for liver cirrhosis: Varices, hepatic encephalopathy, and related complications.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2020 Apr;26(2):83-127. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2019.0010n. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31918536 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Huang Lian Jie Du Decoction Prevents Chronic Alcoholic Encephalopathy and Improves Gut Microbiota Imbalance in Mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jun 25. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-05151-6. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40555894
References
-
- Sharma P, Sharma BC, Sarin SK. Predictors of nonresponse to lactulose in patients with cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010; 22:526–531. - PubMed
-
- American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 practice guideline by the European Association for the Study of the Liver and the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. J Hepatol 2014; 61:642–659. - PubMed
-
- Zhang JY, Kuai JH, Jia JD, et al. The effect of portal hypertension on prognosis in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2009; 17:263–265. - PubMed
-
- Said A, Williams J, Holden J, et al. Model for end stage liver disease score predicts mortality across a broad spectrum of liver disease. J Hepatol 2004; 40:897–903. - PubMed
-
- Wong RJ, Gish RG, Ahmed A. Hepatic encephalopathy is associated with significantly increased mortality among patients awaiting liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 2014; 20:1454–1461. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous