The ARIC-PET amyloid imaging study: Brain amyloid differences by age, race, sex, and APOE
- PMID: 27371485
- PMCID: PMC4970663
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002914
The ARIC-PET amyloid imaging study: Brain amyloid differences by age, race, sex, and APOE
Abstract
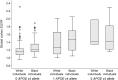
Objective: To evaluate differences in amyloid deposition in a community-based cohort without dementia by age, sex, race, education, and APOE ε4 allele status.
Methods: Recruited from the longitudinal Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study, 329 participants without dementia, ages 67-88 years, were imaged using florbetapir PET at 3 US community sites (Washington County, Maryland; Forsyth County, North Carolina; and Jackson, Mississippi). Standardized uptake value ratios (SUVRs) were calculated; global cortical SUVR >1.2 was evaluated as the primary outcome. Age, race, sex, education level, and number of APOE ε4 alleles were evaluated in multivariable models including vascular risk factors, brain white matter hyperintensity and total intracranial volume, and cognitive status.
Results: A total of 141 of the participants (43%) were black. In multivariable models, odds of elevated SUVR was increased in participants with increasing age (odds ratio [OR] 1.63, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.01-2.65 per 10 years of age) and black race (OR 2.08, 95% CI 1.23-3.51) but did not differ by educational level. Each ε4 allele was associated with increased odds of elevated SUVR (OR 2.65, 95% CI 1.61-4.39).
Conclusions: In this community-based cohort without dementia, florbetapir uptake is associated with older age and APOE genotype. Black race was associated with higher SUVR, after adjusting for demographics, vascular risk factors, cognitive status, white matter hyperintensity volume, and APOE genotype, with effect sizes nearing those seen for APOE ε4. Replication of these findings is needed in other cohorts, and reasons for and consequences of these observed differences by race warrant further study.
© 2016 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures


Comment in
-
A race effect on amyloid deposition?Neurology. 2016 Aug 2;87(5):454-5. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002924. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Neurology. 2016. PMID: 27371492 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kuller LH, Lopez OL, Newman A, et al. . Risk factors for dementia in the cardiovascular health cognition study. Neuroepidemiology 2003;22:13–22. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096812/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096902/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG040282/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096814/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096917/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
