Regulation of Retinoic Acid Inducible Gene-I (RIG-I) Activation by the Histone Deacetylase 6
- PMID: 27372014
- PMCID: PMC4972567
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.06.015
Regulation of Retinoic Acid Inducible Gene-I (RIG-I) Activation by the Histone Deacetylase 6
Abstract
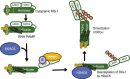
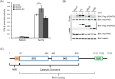
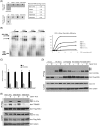
Retinoic acid inducible gene-I (RIG-I) is a cytosolic pathogen recognition receptor that initiates the immune response against many RNA viruses. Upon RNA ligand binding, RIG-I undergoes a conformational change facilitating its homo-oligomerization and activation that results in its translocation from the cytosol to intracellular membranes to bind its signaling adaptor protein, mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein (MAVS). Here we show that RIG-I activation is regulated by reversible acetylation. Acetyl-mimetic mutants of RIG-I do not form virus-induced homo-oligomers, revealing that acetyl-lysine residues of the RIG-I repressor domain prevent assembly to active homo-oligomers. During acute infection, deacetylation of RIG-I promotes its oligomerization upon ligand binding. We identify histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) as the deacetylase that promotes RIG-I activation and innate antiviral immunity to recognize and restrict RNA virus infection.
Keywords: Deacetylation; HCV; HDAC6; Innate immunity; Interferon; RIG-I; West Nile virus.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Histone deacetylase 8 promotes innate antiviral immunity through deacetylation of RIG-I.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jul 5;14:1415695. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1415695. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39035358 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC6 regulates cellular viral RNA sensing by deacetylation of RIG-I.EMBO J. 2016 Feb 15;35(4):429-42. doi: 10.15252/embj.201592586. Epub 2016 Jan 8. EMBO J. 2016. PMID: 26746851 Free PMC article.
-
Self-Recognition of an Inducible Host lncRNA by RIG-I Feedback Restricts Innate Immune Response.Cell. 2018 May 3;173(4):906-919.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.064. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Cell. 2018. PMID: 29706547
-
RIG-I: a multifunctional protein beyond a pattern recognition receptor.Protein Cell. 2018 Mar;9(3):246-253. doi: 10.1007/s13238-017-0431-5. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Protein Cell. 2018. PMID: 28593618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent developments in understanding RIG-I's activation and oligomerization.Sci Prog. 2024 Jul-Sep;107(3):368504241265182. doi: 10.1177/00368504241265182. Sci Prog. 2024. PMID: 39091074 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in the Mechanistic Study of the Control of Oxidative Stress Injury by Modulating HDAC6 Activity.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2023 Mar;81(1):127-139. doi: 10.1007/s12013-022-01125-w. Epub 2023 Feb 7. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2023. PMID: 36749475 Free PMC article.
-
A Cell-Based Screen Identifies HDAC Inhibitors as Activators of RIG-I Signaling.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Feb 14;9:837610. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.837610. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35237663 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase 6's function in viral infection, innate immunity, and disease: latest advances.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 11;14:1216548. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1216548. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37638049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between Autophagy and RLR Signaling.Cells. 2023 Mar 21;12(6):956. doi: 10.3390/cells12060956. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36980296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HDAC6 deacetylates TRIM56 to negatively regulate cGAS-STING-mediated type I interferon responses.EMBO Rep. 2025 Feb;26(3):720-747. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00358-5. Epub 2025 Jan 2. EMBO Rep. 2025. PMID: 39747662 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bantscheff M., Hopf C., Savitski M.M., Dittmann A., Grandi P., Michon A.M., Schlegl J., Abraham Y., Becher I., Bergamini G., Boesche M., Delling M., Dumpelfeld B., Eberhard D., Huthmacher C., Mathieson T., Poeckel D., Reader V., Strunk K., Sweetman G., Kruse U., Neubauer G., Ramsden N.G., Drewes G. Chemoproteomics profiling of HDAC inhibitors reveals selective targeting of HDAC complexes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011;29:255–265. - PubMed
-
- Blander J.M. A long-awaited merger of the pathways mediating host defence and programmed cell death. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014;14:601–618. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

