Clinical benefit of midodrine hydrochloride in symptomatic orthostatic hypotension: a phase 4, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, tilt-table study
- PMID: 27372462
- PMCID: PMC4951503
- DOI: 10.1007/s10286-016-0363-9
Clinical benefit of midodrine hydrochloride in symptomatic orthostatic hypotension: a phase 4, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, tilt-table study
Abstract
Objective: Midodrine hydrochloride is a short-acting pressor agent that raises blood pressure in the upright position in patients with orthostatic hypotension. The US Food and Drug Administration's Subpart H approval, under which midodrine was initially approved, requires post-marketing studies to confirm midodrine's clinical benefit in this indication. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical benefit of midodrine with regard to symptom response.
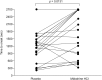
Methods: This was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, crossover, multicenter study (NCT01518946). Following screening, patients aged ≥18 years with severe symptomatic orthostatic hypotension and on a stable dose of midodrine for at least 3 months were randomized to treatment with either their previous midodrine dose or placebo on day 1 and the respective alternate treatment on day 2. The primary endpoint measured time to syncopal symptoms or near-syncope using a 45-min tilt-table test at 1 h post-dose.
Results: Thirty-three patients were screened for inclusion: 19 received at least one dose of midodrine and had at least one post-dose measurement of the primary endpoint. The least-squares mean time to syncopal symptoms or near-syncope after tilt-table initiation (mean ± standard error) was 1626.6 ± 186.8 s for midodrine and 1105.6 ± 186.8 s for placebo (difference, 521.0 s; 95 % confidence interval 124.2-971.7 s; p = 0.0131). There were 15 adverse events in 10 patients; all of these were mild or moderate in severity, with none considered by the investigators to be related to midodrine.
Interpretation: Midodrine is a well-tolerated and clinically effective treatment for symptomatic orthostatic hypotension.
Keywords: Clinical trial; Midodrine; Orthostatic hypotension.
Figures


References
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (2013) ESUOM5: postural hypotension in adults: midodrine. http://publications.nice.org.uk/esuom5-postural-hypotension-in-adults-mi.... Accessed 18 Nov 2014
-
- Schirger A, et al. Midodrine. A new agent in the management of idiopathic orthostatic hypotension and Shy-Drager syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc. 1981;56(7):429–433. - PubMed
-
- Lundbeck LLC (2014) Northera® (droxidopa). Summary of product characteristics. www.drugs.com/pro/northera.html. Accessed 27 Nov 2015
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

