Prevalent, Dynamic, and Conserved R-Loop Structures Associate with Specific Epigenomic Signatures in Mammals
- PMID: 27373332
- PMCID: PMC4955522
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.05.032
Prevalent, Dynamic, and Conserved R-Loop Structures Associate with Specific Epigenomic Signatures in Mammals
Abstract
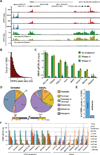
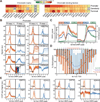
R-loops are three-stranded nucleic acid structures formed upon annealing of an RNA strand to one strand of duplex DNA. We profiled R-loops using a high-resolution, strand-specific methodology in human and mouse cell types. R-loops are prevalent, collectively occupying up to 5% of mammalian genomes. R-loop formation occurs over conserved genic hotspots such as promoter and terminator regions of poly(A)-dependent genes. In most cases, R-loops occur co-transcriptionally and undergo dynamic turnover. Detailed epigenomic profiling revealed that R-loops associate with specific chromatin signatures. At promoters, R-loops associate with a hyper-accessible state characteristic of unmethylated CpG island promoters. By contrast, terminal R-loops associate with an enhancer- and insulator-like state and define a broad class of transcription terminators. Together, this suggests that the retention of nascent RNA transcripts at their site of expression represents an abundant, dynamic, and programmed component of the mammalian chromatin that affects chromatin patterning and the control of gene expression.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Aguilera A, Garcia-Muse T. R loops: from transcription byproducts to threats to genome stability. Molecular cell. 2012;46:115–124. - PubMed
-
- Bell AC, West AG, Felsenfeld G. The protein CTCF is required for the enhancer blocking activity of vertebrate insulators. Cell. 1999;98:387–396. - PubMed
-
- Boguslawski SJ, Smith DE, Michalak MA, Mickelson KE, Yehle CO, Patterson WL, Carrico RJ. Characterization of monoclonal antibody to DNA.RNA and its application to immunodetection of hybrids. J Immunol Methods. 1986;89:123–130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

